ChatGPT and other AI products took the world by storm last year, with fear and doubt warring with excitement about what AI could do for business.
Table of Contents
ToggleAI and robotics offer many capabilities for business executives interested in bringing innovation to their operations.
- AI can consume massive amounts of data to increase efficiency and automate operations. Used well, AI can help organizations automate routine tasks, offer business insights based on data analysis, and personalize the customer experience.
- AI can and already does help with risk management through its ability to analyze patterns and identify anomalies, enabling AI to detect fraud and cyber-attacks.
- Automated demand forecasting, inventory management, and planning of efficient delivery routes enable AI to optimize supply chain and logistics.
AI’s business value lies in its ability to transform operations, drive innovation, enhance customer experiences, and provide actionable insights, all of which contribute to improved performance and competitive positioning.
The State of AI Adoption
At the end of 2023, Atomicwork commissioned a survey with ITSM Tools and asked the IT marketplace and industry experts questions about AI and adoption.
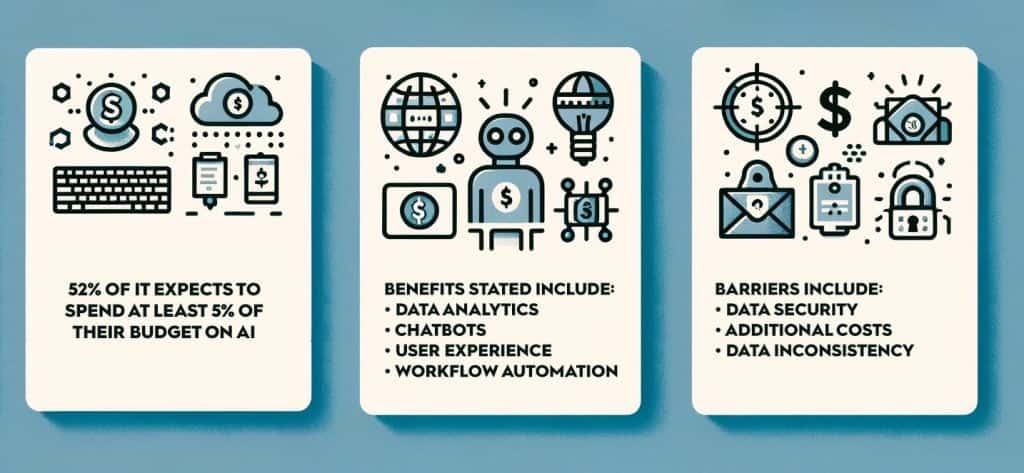
This State of AI in IT survey results identified some critical insights, including:
Although I was a participating industry expert, I wanted to provide a more in-depth view from my perspective on not just what the survey found, but also what I am seeing in the industry.
Adoption Challenges
The fear factor in AI adoption sets the stage for challenges that must be addressed before organizations can successfully adopt AI.
According to the survey, the top three barriers to AI adoption included customer data security, additional cost and the inaccuracy or inconsistency of data. Lack of IT experience with AI was also a concern.
Organizations are addressing this by developing an AI code of ethics governing how customer and other data will be used by AI, who can see and use it and how decisions will be made. This includes defining the types of decisions that will require human oversight.
Successful AI implementation will require organizations to be transparent about their efforts, letting people know where AI is being used and begin in areas where adoption is already assured.
Realizing the Benefits of AI

As an IT thought leader with years of experience in operations, support, and IT strategy, I’ve seen many tools come and go, but I can say AI is one that can transform how business operates, starting with how IT performs.
Data analytics, chatbots, user experience improvements, and automated workflows already have general acceptance and are present in many modern ITSM tools.
Some clear use cases can help IT organizations get started.
Data Analytics and Workflows
AI can explore mountains of data, far too much for humans to understand. This leads to several solutions to issues with which IT has historically struggled:
- Going beyond asset management to build a complete configuration management database (CMDB), with information about each device down to the desktop and mobile device level.
- Using information in the CMDB, patch management tools, and data from multiple monitoring systems to identify and address errors and configuration issues before they cause service interruptions.
- Using automated workflows to achieve power automated resolution and opening tickets to the correct technical team when they cannot.

To start this, IT organizations that have already implemented a CMDB with automated discovery tools can build AI dashboards to identify configuration items (CIs) with data issues, eliminate duplicates, and identify CIs with incomplete information.
These AI-driven analytics dashboards use your data and defined rules to identify and display issues for follow-up and can even be configured to open tickets for investigation.
Incident avoidance grows from here. Imagine creating device health dashboards and using workflows to correct issues or open tickets for their correction automatically. This enables IT to manage operations by dealing with exceptions before they affect end-user services. AI should drive pro-active ITSM from most companies’ traditional reactive model.
AI Chatbots
Organizations have struggled to implement chatbots because they rely on knowledge bases that may not yet exist or use pre-determined conversations to answer questions. The result is a minimally effective channel that ultimately leads to frustration.
Now that ChatGPT and similar AI-enabled chatbots have become part of our daily lives, their functionality can be leveraged to search the Internet as well as internal documentation and unstructured knowledge repositories for known solutions to common problems and present them to end users as part of the chatbot’s routine.
For example, typing “How do I add a signature to Outlook?” brought back an immediate response from ChatGPT that provided accurate instructions for both the desktop and web versions of Outlook, eliminating the most common issue with chatbot adoption: lack of knowledge.
AI and the User Experience
Pulling next-gen AI tools together with the channels used to provide employee or customer support transforms the user experience. The service portal has long been the central hub for online support and self-service, but ITSM and Customer Service solutions can now integrate easily with corporate messaging tools like Teams and Slack.
A more innovative approach to engagement now includes chatting with a support channel in conversational terms and getting results. Instant messaging (IM) platforms like Teams and Slack, integrated with AI and the service portal, enable users to:
- Answer questions and get instructions: Integrations enable the end user to enter a question or need into Teams or Slack and get an answer to the question either from an internal knowledge base, ticket solutions, or a product that works like ChatGPT in the previous example.
- Log an issue: When a conversation doesn’t resolve an issue, the end user can opt to log an incident ticket or speak with a human.
- Make an appointment for the walk-up center: If certain situations require hands-on work, the IM product can set an appointment for the end user or put them on a list using a pre-configured workflow.
- Log a request: End users who need to submit a request can do it via chat. The chatbot may ask some follow-up questions and then log a request. While this leverages some service portal capabilities, it may be a more friendly interface for many end users.
The Value of AI for the End User Experience
This next generation of AI tools creates a game-changing user experience. Vijay Shankar argues that the service portal is dead because conversational AI use with corporate IM platforms eliminates the need to use the portal. This may be premature (you need the back-end portal to achieve this), but corporate chat is clearly a critical channel for organizations to make available as part of a holistic support experience.
You can also argue that problem management is dead because using AI for configuration, patch management, and proactive device management eliminates incidents before they become problems.
One thing is clear: AI offers organizations the ability to transform the operational and support environments, often with little to no investment other than time and training. This transformation can be significant when savings from increased user productivity and lowered downtime are considered.
Envision your organization’s future with AI.
Read more about the State of AI in IT today!