Key Highlights
- Business Continuity Management (BCM) is a strategic framework for enabling organizations to rapidly restore their operations after a disaster.
- BCM includes risk management processes and procedures that aim to prevent interruptions to mission-critical services and reestablish full day-to-day function in the organization.
- Key components of a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) include conducting risk assessments, performing business impact analysis, and developing a comprehensive business continuity plan.
- Implementing a BCMS involves aligning with ISO 22301 standards and regularly reviewing and updating the system for continual improvement.
Introduction
We live in a volatile and uncertain world. In this volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) environment, a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) ensures continued operations during disasters by enabling rapid service restoration based on business resilience.
Table of Contents
ToggleThis is achieved by developing strategies to mitigate risks and maintain critical functions. Business Continuity Planning addresses unpredictable events like natural disasters, cyber-attacks, and pandemics to ensure smooth operation during disruptions.
Implementing a BCMS is crucial for organizational resilience and crisis management. It helps organizations maintain resiliency in responding quickly to interruptions, saves money and time, and improves communication, technology, and resilience.
A comprehensive BCMS includes conducting risk assessments, performing business impact analysis, and developing a business continuity plan.

What is a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS)?
A Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) is a structured and proactive approach to managing business operations during and after a crisis or disruption. It is designed to identify potential risks, assess their impact on business operations, develop strategies to mitigate them and ensure the continuity of critical business functions through continuous improvement.
At its core, a BCMS is a management system that integrates business continuity planning, disaster recovery, and risk management. It provides a systematic approach to identify, analyze, and respond to potential threats and disruptions. The goal of a BCMS is to enable organizations to continue operating at an acceptable level during a crisis and recover quickly to normal operations.
What does a BCMS include?
A BCMS typically includes the following components:
- Risk Assessment: Potential risks and threats to the organization are identified along with their likelihood and potential impact. This is used to prioritize them based on their significance.
- Business Impact Analysis: Evaluating the potential impact of a disruption on critical business functions and determining the resources and strategies needed to recover.
- Incident Response and Recovery: Developing a comprehensive response plan, establishing a crisis management team, and implementing strategies to manage and recover from disruptions.
- Communication and Training: Developing a communication plan that ensures effective internal and external communication during a crisis and training employees on their roles and responsibilities during a disruption.
- Testing and Continual Improvement: Regular testing and exercises are essential to ensure the BCMS’s effectiveness. This includes conducting drills, tabletop exercises, and scenario-based simulations to identify gaps and improve response capabilities then continually reviewing and updating the BCMS to incorporate lessons learned and new best practices.

The Importance of BCMS in Organizational Resilience
Organizational resilience is the ability to withstand and recover from disruption, adapt to change, and grow stronger in adversity. Organizations face numerous challenges, from natural disasters and cybersecurity threats to supply chain disruptions and pandemics. A Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) ensures organizational resilience.
Benefits of a BCMS
By implementing a BCMS, organizations can minimize the impact of disruptions on their operations, employees, customers, and stakeholders in the following ways:
- Maintain Normal Operations: Organizations can minimize downtime and financial losses by identifying critical business functions and developing strategies to ensure their continuity.
- Respond to Natural Disasters: A BCMS helps organizations develop strategies for responding to natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods by providing evacuation plans, alternate work locations, and data backup and recovery procedures.
- Manage Crisis Situations: A BCMS helps organizations establish protocols and procedures to manage crisis situations like cybersecurity attacks or public health emergencies, including incident response plans, communication strategies, and resource allocation.
- Enhance Customer Confidence: Implementing a BCMS demonstrates a commitment to continuity and resilience. It enhances customer confidence and trust, resulting in customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Aligning BCMS with ISO 22301 Standards

Aligning a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) with ISO 22301 standards is a best practice for organizations seeking to enhance their business continuity capabilities. ISO 22301 is an international standard that provides guidance and requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving a BCMS.
By aligning with ISO 22301, organizations can ensure that their BCMS meets internationally recognized standards and best practices.
Elements of ISO 22301
ISO 22301 provides a framework for establishing a BCMS that includes guidance to organizations in the following key areas:
- Policy and Objectives: Organizations must establish a clear policy and objectives for their BCMS, outlining their commitment to business continuity and their goals for maintaining critical operations during and after a disruption.
- Risk Assessment and Management: Organizations must conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities, including the likelihood and risk of each.
- Business Impact Analysis: Organizations must perform a business impact analysis to identify critical business functions and their dependencies to help prioritize resources and recovery strategies.
- Business Continuity Planning: Organizations must develop and implement a comprehensive business continuity plan that outlines the procedures and recommendations for handling emergencies.
- Testing and Continual Improvement: Organizations must regularly test their BCMS to ensure its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Key Components of a BCMS
A Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) includes several key components that work together to ensure the continuity of critical business functions during and after a disruption.
These components include:
- Risk assessments to help identify potential risks and vulnerabilities.
- Business impact analysis to identify critical business functions and their dependencies.
The business continuity plan outlines the procedures and recommendations for handling emergencies, including recovery strategies, roles and responsibilities, and resource availability.

Conducting Risk Assessments for Proactive Management
The goal of risk assessments is to enable organizations to make informed decisions about risk mitigation strategies.
Conducting risk assessments is a critical component of a proactive Business Continuity Management System (BCMS). By identifying potential risks and understanding their impact on business operations, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate them and ensure the continuity of critical business functions.
Risk assessments involve systematically identifying, analyzing, and evaluating potential risks. This includes assessing each risk’s likelihood and potential impact, determining the risk tolerance level, and prioritizing risks based on their significance.
Once the risk assessment is complete, controls and safeguards can be implemented.

The Role of Business Impact Analysis in BCMS
Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is a crucial component of the Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) helping organizations identify critical business functions and their dependencies. By understanding the potential impact of a disruption on these critical functions, organizations can develop strategies to prioritize resources, allocate roles and responsibilities, and ensure the continuity of operations.
The BIA process involves analyzing the financial, operational, reputational, and regulatory consequences of service disruption by:
- Identifying and analyzing critical business functions
- Determining their dependencies on other functions
- Assessing their potential impact on the organization.
The information gathered through the BIA process is used to develop recovery strategies, establish recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs), and prioritize the allocation of resources during a crisis.

Developing a Comprehensive Business Continuity Plan
Developing a comprehensive Business Continuity Plan (BCP) is crucial in implementing a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS).
A BCP outlines the procedures and recommendations for handling emergencies and ensures that the organization can continue operating during and after a service disruption.
Having a plan also ensures that staff can be trained to carry it out effectively in the event of a disaster.
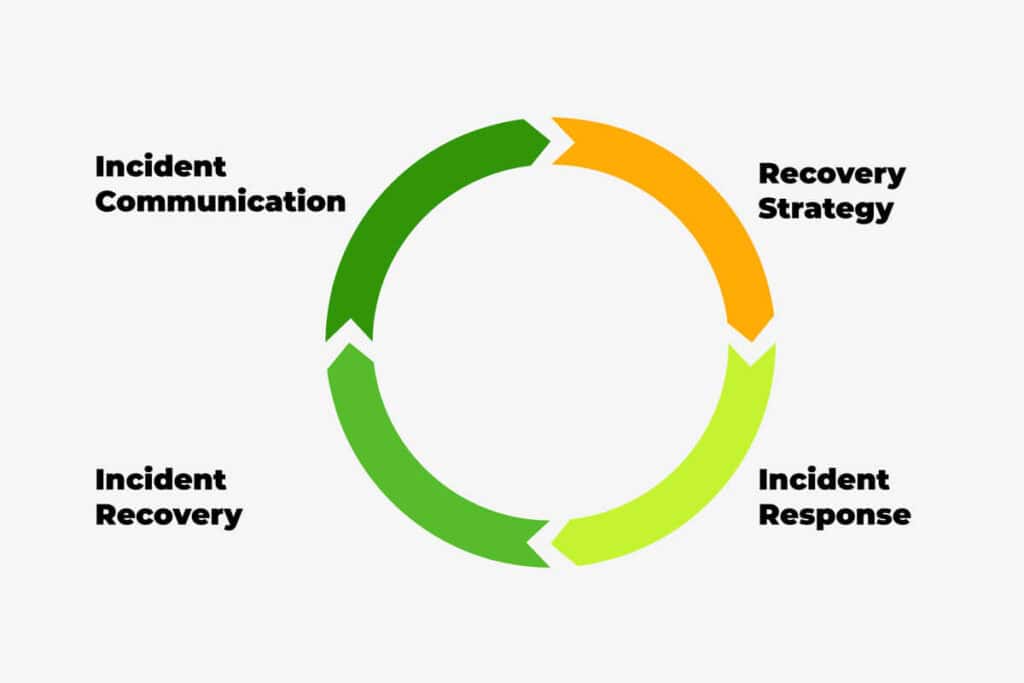
Elements of a BCP
A comprehensive BCP includes the following key elements:
Recovery Strategies: The BCP identifies the strategies and approaches to recover critical business functions and restore normal operations. This includes establishing recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) to guide the recovery process.
Incident Response: The BCP outlines the procedures and protocols to be followed during a crisis, including establishing a crisis management team, defining roles and responsibilities, and implementing communication protocols.
Incident Recovery: The BCP specifies the resources and equipment needed for incident recovery, coordinating recovery efforts, and monitoring progress.
Incident Communication: The BCP establishes communication protocols and channels for internal and external communication with stakeholders, customers, and the public during an incident or crisis.

Strategy Formulation for Effective Response and Recovery
Strategy formulation is a critical component of an effective Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) and involves developing strategies for responding to and recovering from potential disruptions.
This includes identifying critical business functions, establishing recovery time objectives (RTOs), and formulating strategies to ensure these functions’ effective response and recovery.
Effective response and recovery strategies involve the following key elements for incident response:
- Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs): This defines the time between a disruption and the resumption of critical business functions. Strategies are formulated to prioritize the recovery of essential functions based on their RTOs.
- Recovery Strategies outline the steps and actions needed to restore critical functions and normal operations.

Critical Functions and Services During Crises
Certain functions and services become critical for an organization’s survival and recovery during a crisis or disruption. They play a vital role in maintaining operations and ensuring the continuity of service. Some key considerations for critical functions and services during crises include:
- Essential Services: Identify essential services, such as IT infrastructure, communication systems, and customer support, that must be maintained during a crisis.
- Business Recovery: Develop strategies and plans to recover critical business functions and processes, prioritizing those essential for the organization’s survival and recovery.
- Event or Disaster: Establish protocols and procedures for managing and responding to a disaster, including emergency response plans, evacuation procedures, and alternate work locations.
- Business Continuity Planning: Ensure that critical business functions are included in the organization’s business continuity plan, with detailed steps and actions for recovery and resumption.

Tools and Support for Implementing BCMS
Implementing a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) requires tools and support to ensure its effective development, implementation, and management. These provide organizations with a strategic approach to business continuity and enable them to maintain the continuity of critical business functions during and after a disruption.
Some key tools to consider include:
- Business Continuity Management Software (BCMS) provides a centralized platform for managing all aspects of business continuity planning: risk assessments, business impact analysis, incident response, and recovery strategies.
- Tools for Risk Assessment: These tools help organizations identify and assess potential risks and vulnerabilities, providing a structured approach to risk assessment that enables organizations to prioritize risks and develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
- Incident Management: These tools facilitate incident management and tracking and help organizations coordinate response and recovery efforts. They provide a centralized platform for documenting incidents, assigning tasks, and monitoring progress.
- Training and Support: Training and support resources help organizations implement and maintain their BCMS effectively. This includes training programs for employees on their roles and responsibilities in times of crisis and ongoing support from experts in business continuity planning and management.
Conclusion
A Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) is not just a protocol; it’s a strategic shield against unforeseen disruptions that can affect organizational resilience.
Businesses can proactively safeguard critical functions during crises by aligning with ISO 22301 standards, conducting risk assessments, and formulating comprehensive continuity plans. Regular reviews and updates are key to achieving BCMS certification and ensuring preparedness. Embracing BCMS is a proactive approach to mitigating risks and enhancing business sustainability in an ever-evolving landscape of uncertainties.
Frequently Asked Questions

How Does BCMS Prepare Organizations for Unforeseen Disruptions?
A BCMS helps organizations prepare for unforeseen disruptions by identifying potential risks, developing recovery strategies, and establishing protocols for responding to and recovering from crises. It ensures the organization can maintain critical operations and minimize downtime during a disruption.
What Are the First Steps in Developing a BCMS?
The first steps in developing a BCMS include conducting a risk assessment to identify potential risks, performing a business impact analysis to determine critical functions, and aligning with ISO 22301 standards for best practices and regulatory compliance.
How Often Should a BCMS Be Reviewed and Updated?
A BCMS should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure continual improvement and alignment with changing business needs and regulatory requirements. It is good practice to conduct reviews at least annually or whenever significant changes to the organization or its operations occur.
Can Small Businesses Benefit from Implementing a BCMS?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from implementing a BCMS. A BCMS helps small businesses develop a business continuity strategy, improve their resilience, enhance customer confidence, and ensure the continuity of critical operations during and after a disruption.




