Understanding ITSM and Its Strategic Importance
What is the meaning of ITSM?
Table of Contents
ToggleITSM (IT Service Management) is a proven and comprehensive approach for managing and delivering IT services used by many thousands of successful businesses worldwide.
This article will give you insights into how ITSM can help your business.
So read on if you want to understand more about what ITSM is, what the key components are, and how it can be used to deliver your organization’s goals and customer needs.

Why do I need ITSM as well as IT?
When discussing the ITSM meaning, it is important to note that excellence in IT needs more than just good technical support. It also requires management of the full IT lifecycle, and a complete integration into the wider business, ensuring efficient services that deliver value and satisfy customers.
The media regularly publishes examples of high-profile IT failures that cost companies thousands of dollars.
Investing in IT technology alone will not protect your business from failures like these.
Investment in ITSM is equally, if not more, important for any organization that wants to stay competitive and leverage its investment in IT.
Why do I need to Align IT Services with Business Goals?
Ensuring that IT services support business objectives is a fundamental principle of ITSM.
This alignment allows businesses to utilize IT as a strategic asset, fostering innovation and creating a competitive advantage. Today’s top companies, including Google and Amazon, have recognized this, streamlining delivery, enhancing service quality, and effectively managing the IT lifecycle using ITSM practices.
A strategic alignment of IT with the rest of the business enables organizations to rapidly and safely adapt to changing demands, leveraging ITSM not just for operational efficiency but also for long-term business success.
What is the difference between a Service Desk and ITSM?
The service desk is a vital function in ITSM, providing the contact point for users of IT systems.

It can transform how users view IT, by providing crucial support to resolve issues, process customer service requests, and provide other help and support.
With responsibility for incident management and service request management it:
- logs, tracks, and resolves IT issues
- manages requests for hardware, software, and access.
IT service management is much more than just an IT service desk and incident management, but this is where most organizations start. The Evolution and Importance of ITSM
The progression of ITSM has been remarkable, especially in recent years. Changes in technologies, development, project management, and operational approaches have forced a fundamental rethink. For example, new versions of applications are now delivered in days or hours instead of weeks or months.
Initially, ITSM, especially ITIL and ISO20000, focused primarily on optimizing internal IT processes and management of IT infrastructure, against a background of inflexible and cumbersome application development approaches.
However, with digital transformation reshaping businesses, ITSM has now evolved to play a more strategic role. It now encompasses and enriches today’s technologies and delivery methodologies, enhancing agility, efficiency, and competitiveness while managing the risks that speed and flexibility bring.

What are the Key Components of Effective ITSM?
Effective ITSM is built on four key pillars: people, processes, partners, and technology, accompanied by a defined service lifecycle.
Each plays a crucial role in the successful management delivery of IT services.
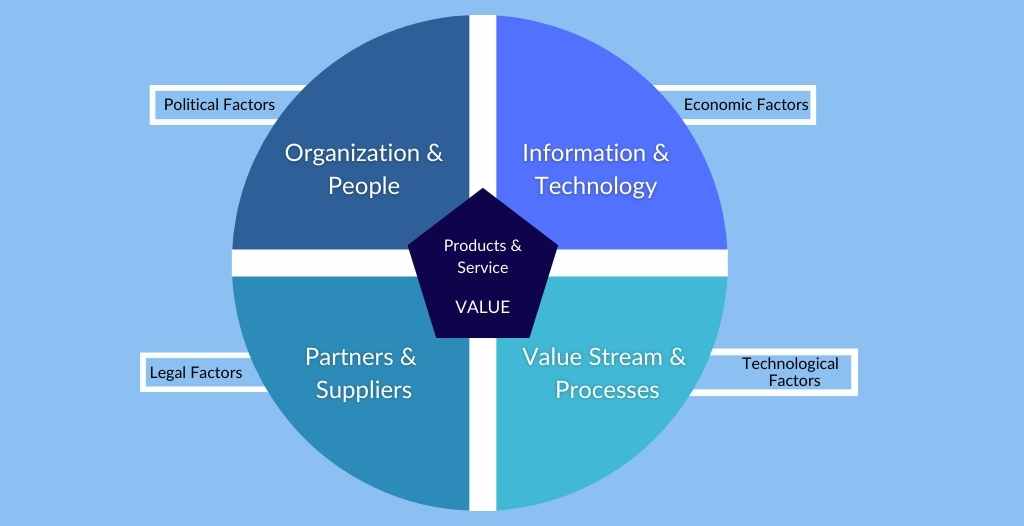
People
IT staff and end-users are central to ITSM, ensuring that services meet user needs and expectations.
Processes
Processes (sometimes called practices) provide a structured and repeatable approach to managing services efficiently and effectively.
Partners
Just about every business relies on other organizations for IT. That includes purchase and support of IT products, using IT services provided through the Cloud, and outsourcing activities like support.
Technology
ITSM software and tools support the processes and integration with people and partners, enabling automation, monitoring, and reporting.
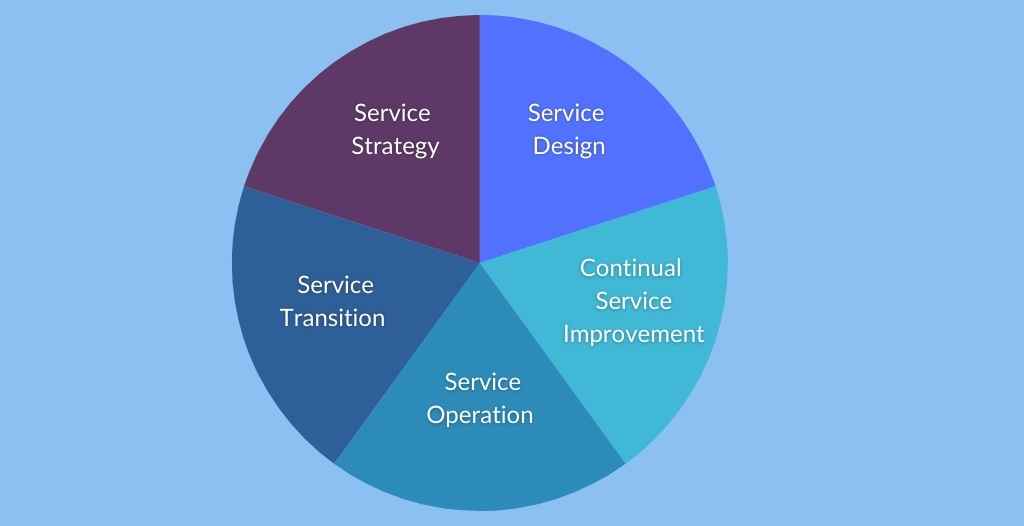
Service Lifecycle
Implementing ITSM involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses all of these four pillars within a service lifecycle. The lifecycle typically includes service strategy and service design, where the focus is on aligning IT services with the objectives of the business; service transition, where services are developed and deployed; and service operation, where ongoing management and support of services take place.
Each phase of the lifecycle is crucial for ensuring that IT services are effective, reliable, and capable of evolving with the business’s needs.
ITSM Processes: Ensuring Efficient Service Delivery
ITSM processes are fundamental to efficient IT service delivery, encompassing a range of activities that ensure each IT service can meet both business and customer needs.
Typical ITSM processes include:
- incident management, which focuses on quickly resolving IT issues;
- service request management, which handles user requests for access to resources
- problem management, aimed at identifying and addressing the root causes of incidents;
- change management and asset management, which ensure that changes to each IT service are made in a controlled and efficient manner;
- configuration management, which maintains accurate records of all IT assets;
- financial management, gathering information on the costs of IT services;
- capacity management, ensuring that IT services always have sufficient capacity;
- and more.
The Role of ITSM Software in Service Management
ITSM software is vital in today’s IT service management landscape.
ITSM tools automate and streamline ITSM processes, making them more efficient and effective.
From managing incidents to monitoring capacity, ITSM software plays a critical role in enhancing service management capabilities.

Key Features and Benefits of ITSM Software
The capabilities of many ITSM software tools extend beyond basic service desk functions, encompassing a wide array of tools and functionalities that collectively enhance and support many service management processes.
By leveraging these tools, IT organizations can not only improve their service delivery, but also align their services more closely with the strategic objectives of their businesses, leading to greater overall success and customer satisfaction.
Service Desk Functionality
- Features: This includes ticketing systems for incident management and service request management, self-service, automated routing and escalation, and self-service portals for end-users.
- Benefits: The functionality improves response times, enhances communication between IT staff and end-users, and streamlines the resolution process, leading to increased satisfaction and efficient self-service, incident, and service requests resolution.
Asset Management Capabilities
- Features: ITSM software offers tools for tracking and managing both hardware and software assets. This includes inventory management, license management, and lifecycle management.
- Benefits: Asset management capabilities ensure optimal utilization of IT resources, reduce costs associated with over or under-purchasing and maintain compliance with licensing agreements.
Knowledge Management Tools
- Features: These tools facilitate the creation, storage, and sharing of IT knowledge, including solution databases, service catalogs, FAQs, links with problem management, and documentation repositories.
- Benefits: Knowledge management enhances the efficiency of services by promoting self-help among users, reducing repetitive inquiries, and preserving valuable IT knowledge.
Configuration Management
- Features: Configuration management involves maintaining information about IT assets and configurations within an environment. This often integrates with a Configuration Management Database (CMDB).
- Benefits: This feature provides visibility into the IT infrastructure, enabling better decision-making, supporting change management, and reducing the risks associated with changes and configurations.
Reporting and Analytics
- Features: Advanced reporting capabilities and analytics tools provide insights into IT service performance, incident patterns, and customer metrics.
- Benefits: These insights help in making data-driven decisions, identifying areas for continual improvement, and optimizing processes.
Workflow Automation and Orchestration
- Features: This includes automating routine tasks and orchestrating complex workflows across various IT service management processes.
- Benefits: Automation reduces manual efforts, minimizes errors, and accelerates delivery, while orchestration ensures that different processes work in harmony for seamless service management.
Integration Capabilities
- Features: ITSM software often integrates with other business and IT tools, such as CRM systems, project management software, and development tools.
- Benefits: Integration enables a more unified approach to IT service management, enhancing collaboration across departments and aligning services more closely with objectives.
Change Management and Release Management
- Features: These functionalities manage the process of making changes to the IT environment and releasing new software or updates.
- Benefits: Effective change management and release management ensure that changes are implemented smoothly without disrupting service, maintaining service stability and reliability.
Incident and Problem Management
- Features: These features focus on managing and resolving incidents and identifying and addressing the root causes of problems.
- Benefits: They ensure quick restoration of services after incidents and help prevent the recurrence of problems, improving the overall quality of IT services.
Customer Feedback and Customer Satisfaction Tracking
- Features: Tools for collecting and analyzing customer feedback on every IT service.
- Benefits: This feedback is crucial for continuous improvement and for aligning services more closely with user needs and expectations.
Aligning ITSM with Business Strategy
Aligning IT service management with business strategy is crucial for leveraging IT as a strategic tool for business growth. ITSM plays a pivotal role in ensuring that IT services support and advance business goals, from enhancing operational efficiency to fostering innovation and competitive advantage.

Through strategic ITSM, organizations can achieve a closer alignment between their IT operations and their business objectives. This alignment ensures that IT services are not just efficient but also contribute significantly to achieving the organization’s goals.
ITSM’s role in this strategic alignment is vital for organizations to remain agile, responsive, and competitive in today’s business environment.
Understanding ITSM Frameworks
ITSM frameworks, such as ITIL (formerly the Information Technology Infrastructure Library) and the Microsoft Operations Framework, offer structured guidance for implementing effective ITSM.
Each ITSM framework provides a set of best practices and processes that can give organizations a proven template for managing IT services.

Key Principles of Popular ITSM Frameworks
Frameworks like ITIL focus on service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual service improvement, offering a comprehensive approach to ITSM systems.
They emphasize the importance of aligning IT services with the goals of the business, managing IT services effectively, and continually improving delivery.
Adopting these frameworks helps organizations standardize their ITSM practices, leading to improved efficiency and service quality.
Types of ITSM Frameworks
Various ITSM (IT Service Management) frameworks have been developed over the years to guide organizations in effectively managing their IT services. Each framework offers a unique set of principles, best practices, and processes.
Each of these frameworks has its own strengths and can be chosen based on the specific needs, size, and nature of the organization’s IT environment.
Here’s a list of some of the most prominent ITSM frameworks:
ITIL
The ITIL framework, formerly known as the Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is perhaps the most widely recognized ITSM framework, providing a comprehensive set of guidelines for managing IT services. It focuses on aligning IT services with business needs and emphasizes continuous improvement.
Microsoft Operations Framework (MOF)
Developed by Microsoft, MOF integrates ITIL principles based on ITIL processes with Microsoft’s own best practices. It’s designed to provide guidance across the entire IT lifecycle for Microsoft technologies.
Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology (COBIT)
COBIT is a framework developed by ISACA for IT governance and management. The scope is broader than the ITIL processes, focusing on regulatory compliance, risk management, and aligning ITSM strategy with business objectives.
ISO/IEC 20000
This is an international IT standard that specifies requirements for an organization to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve a service management system (SMS). It is closely aligned with the principles of ITIL.
Lean IT
Based on the principles of Lean manufacturing, Lean IT focuses on improving efficiency and effectiveness in IT processes, reducing waste, and maximizing value.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a set of techniques and tools for process improvement, originally developed for manufacturing but now applied in various sectors including IT. It aims for near-perfect quality in IT service delivery.
FitSM
This is a lightweight, pragmatic ITSM framework with a focus on being simple and practical. It’s particularly suitable for smaller organizations and those new to ITSM.
VeriSM
An IT service management approach that integrates various frameworks and management practices such as Agile, Lean, and ITIL into a flexible model for delivering digital services.
Business Process Framework (eTOM)
Developed by the TM Forum, eTOM is a comprehensive framework for telecom service providers. It’s used to improve the way telecom companies manage their business operations.
DevOps
While primarily a set of practices for software development and operations teams, DevOps influences ITSM by emphasizing continuous improvement, automation, and collaborative working between development, IT operations teams, and other IT teams.
Service Integration and Management (SIAM)
This management methodology focuses on managing multiple service providers and integrating the services from each service provider and internal IT teams to provide the user with the impression of a single IT service provider and IT organization.
ITSM in the Age of Digital Transformation
In the era of digital transformation, the ITSM meaning is changing and is more crucial than ever. It not only manages IT services but also supports and drives digital initiatives that are key to business innovation and growth.
Effective ITSM ensures that IT services are scalable and adaptable, enabling organizations to embrace new technologies and digital processes.
By integrating ITSM with digital transformation strategies and by extending the scope to enterprise service management, organizations can ensure their IT services are future-ready. This involves adopting new technologies like AI and cloud computing and aligning IT services with emerging business models. ITSM’s role in this context is to facilitate a seamless transition to digital, ensuring that IT services continue to support business objectives in the digital age.
The Future of ITSM in Business
As we look toward the future, the significance of the ITSM meaning in business operations is poised to grow. Emerging technologies and trends are reshaping the ITSM landscape, requiring a more adaptive and innovative approach to managing IT services.
The future of ITSM will be marked by its adaptability to changes such as AI integration, cloud computing, and the increasing importance of cybersecurity.
Organizations that embrace these evolving aspects of ITSM will find themselves better equipped to handle the complexities of a technology-driven business world, achieving not just operational efficiency but also long-term strategic success.




