Technical failures are no longer an option in a business environment that relies on technology for everything, including the revenue stream. Still, business continuity requires more than securing technology from disasters. Unlike disaster recovery planning, business continuity plans involve more than recovering IT systems and their data. Instead, a good BCP will address common business risks and ensure a response that stabilizes business operations, including technology and other factors. So, to create a solid strategy we need to answer the question what does a business continuity plan typically include?
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Business continuity plans help manage the risks businesses face from interruptions due to natural and man-made disasters, cyberattacks, and pandemics. Their goal is to manage risks affecting all areas of business operations.
Due to the complexity of developing, documenting, and testing a plan of this scale, their complexity often leads to organizations failing to plan.
This article simplifies what’s in a typical business continuity plan.
What Is Business Continuity Planning (BCP)?
Business continuity planning (BCP) ensures key business functions continue during disruptions, minimizing downtime and financial losses. This includes identifying threats, assessing risks, and preparing mitigation strategies. An essential step is a risk assessment to pinpoint potential interruptions, helping organizations grasp their risks and plan ways to handle them effectively.

What Does a Business Continuity Plan Typically Include?
Business continuity plans typically include elements essential for ensuring the continuity of critical business functions during and after a service interruption. These elements encompass operational (non-technical) and technical aspects of the organization’s day-to-day activities.
Business continuity plans evaluate risks, developing and then document mitigation and communication strategies for data backup, disaster recovery, cybersecurity, and facility damage by including the following key items:
- Risk assessment: Identifying and documenting potential threats and risks that could disrupt business operations, such as natural disasters, cyber-attacks, or supply chain interruptions.
- Business impact analysis and recovery objectives: Determine and document the impact of disruptions on key business processes, set recovery objectives to prioritize service restoration, minimize downtime, and minimize financial losses.
- Business continuity strategies: Establish backup procedures or remote work protocols to ensure that strategic business operations can continue during and after disruption.
- Crisis management and communication plans: Provide instruction on responding to crises, including clear communication plans to keep employees, stakeholders, and customers informed during a disruption.
- Documentation of the business continuity plan: Creating manuals that include procedures, contact information, and recovery strategies is essential to ensure a quick and effective response during a crisis.
- Training and awareness: Help employees understand their roles and responsibilities during a crisis and raise awareness about the importance of business continuity planning throughout the organization.
- Regular review and updates: Testing and review are critical to ensuring the business continuity plan reflects changes in the business environment, technology, or financial risks and remains effective and relevant.
Structuring the Business Continuity Team
A business continuity plan involves various stakeholders for successful implementation. The structure of the continuity team is vital for effective coordination.

Chief Risk Officer’s Responsibilities
The Chief Risk Officer (CRO) plays a vital role in business continuity planning and risk management. Their responsibilities include:
- Conducting risk assessments and collaborating with senior management to integrate risk management into the organization’s overall strategy.
- Developing strategies for mitigation and preparedness to ensure the continuity of critical business functions.
- Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of risk management measures.
- Keeping senior management informed about potential risks and recommending appropriate actions.
- Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements related to risk management.
The CRO’s expertise and leadership are essential for establishing a robust business continuity plan that addresses the organization’s risks and ensures the continuity of critical business functions.
Business Continuity Manager’s Role
The Business Continuity Manager is responsible for the day-to-day management of the business continuity plan, including:
- Overseeing the development and implementation of the business continuity plan.
- Conducting regular assessments to identify vulnerabilities and improvements in the plan.
- Coordinating with various departments and stakeholders to ensure the plan’s effectiveness.
- Developing proactive measures to mitigate risks and ensure the continuity of critical business functions.
- Training and educating employees on their roles and responsibilities during a disruption.
- Conducting drills and simulations to test the plan’s effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
- Maintaining documentation and records related to the business continuity plan.
Human Resources Role in Business Continuity
Human Resources (HR) is crucial in operationalizing a business continuity plan. They are responsible for ensuring all staff members know the plan and their roles during disruption and are cared for in the event of an emergency when they are on-site.
Facilities Management Role
Facilities Management manages the physical infrastructure, facilities, and equipment that support the organization’s operations. Their key business continuity planning responsibilities include:
- Collaborating with suppliers and partners to identify and address potential risks and disruptions in the supply chain.
- Regularly inspecting and maintaining facilities and equipment to minimize the risk of disruptions.
- Developing and implementing plans for responding to and recovering from disasters that may affect the organization’s facilities and operations.
Developing Critical Business Continuity Strategies
Developing effective business continuity strategies ensures critical business functions continue during disruptions. Two critical strategies include IT disaster recovery plans and crisis communication plans.
Downtime Mitigation with an IT Disaster Recovery Plan
The IT Disaster Recovery Plan focuses on IT system and data recovery post-disaster, incorporating data backup, recovery strategies, and data protection to ensure quick operation restoration.
Key elements of an effective IT disaster recovery plan include:
- Data backup: Frequent backups of all critical business data with off-site storage.
- Recovery Strategies and Redundancy: Strategic decisions and procedures for restoring IT operations or establishing redundant systems and failover mechanisms to ensure continuous IT operations.
- Data protection: Implementing measures to protect sensitive information from loss or unauthorized access.
- Testing and validation: Regularly testing the IT disaster recovery plan to identify weaknesses and ensure effectiveness.
- Documentation: Maintaining detailed documentation of IT systems, recovery procedures, and contact information for internal and external partners.

Crisis Communication Plans for Effective Business Operations
Crisis communication plans outline how the organization will communicate with internal and external stakeholders, ensuring timely and accurate information flow. An effective crisis communication plan includes the following:
- Identifying individuals representing the organization and communicating with internal and external stakeholders.
- Determining the appropriate communication channels, such as email, phone, or messaging platforms.
- Procedures for handling employee notification, including their roles and necessary safety measures.
- Protocols for communicating with external stakeholders, such as customers, suppliers, regulatory bodies, and the public.
- Templates and guidelines for crisis communications to ensure consistent and effective messaging.
- Employee training and drills to help them understand their roles and responsibilities.
Continuous Improvement and Audit Compliance
Continuous improvement and auditing compliance are vital in business continuity planning. Organizations must regularly assess compliance and enhance their plans to meet standards and regulations.
Over time, as operational resilience is ensured through regular updates to address emerging threats and changes, conducting audits helps ensure compliance and identifies areas for enhancement.
Aligning with International Standards
Aligning with an international standard makes it easier for organizations to engage in business continuity planning by providing a framework they can use in their planning process. Standards can help organizations develop a robust business continuity plan that ensures the organization’s ability to continue operations during and after disruptions.
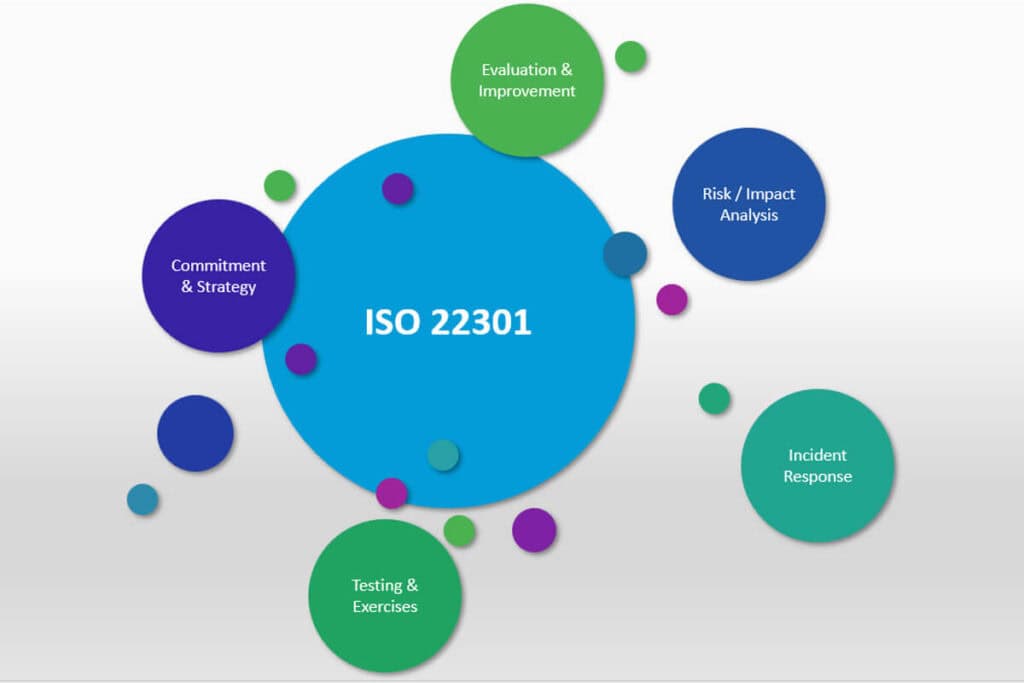
The ISO 22301 Standard for Business Continuity Plan
ISO 22301 is an international standard that provides a framework for establishing, implementing, and maintaining a business continuity management system (BCMS).
The key components of ISO 22301 include many of the items addressed in this article:
- Leadership commitment
- Risk assessment and treatment
- Business impact analysis
- Business continuity strategies
- Incident response and recovery
- Testing and exercises
- Performance evaluation
- Continuous improvement

Updating Backup Plans to Address Emerging Threats
Business continuity plans must be regularly updated to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Risks and disruptions can evolve over time, and organizations must adapt their plans to ensure their continued effectiveness.
Regular updates to the business continuity plan involve:
- Identifying emerging threats:
- Updating risk assessments
- Developing response strategies
- Implementing proactive measures
- Regular plan reviews
The Business Value of Good BCDR Planning
Understanding the nuances between business continuity planning and disaster recovery ensures that organizations are ready when a problem strikes.
IT is familiar with and works towards ensuring system availability through disaster recovery, but often, their business partners fail to plan accordingly. By ensuring a business continuity plan is in place and able to be executed, business executives secure the revenue stream and future of the organization.
Conclusion
A well-thought-out business continuity plan is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring resilience in unexpected disruptions.
Businesses can proactively address challenges and maintain operational continuity by incorporating key elements such as risk assessment, crisis communication strategies, and IT disaster recovery plans.
Structuring a dedicated team, aligning with industry standards like ISO 22301, and continually updating plans to address emerging threats is crucial for effective business continuity management.





