1. Introduction to ITSM / Service Management
Do you want to know more about mastering ITSM (Information Technology Service Management)? Then read on!
Table of Contents
ToggleIn this first article, I will give you an overview of IT service management, why you need to learn more about it, what the top tools are, and more. This will help you to decide which strategy is best for your organization.
Further articles will dive further into the topic, providing increasing levels of detailed information that you can use to improve your business.
What is the meaning of ITSM?
IT service management is a set of interrelated activities, processes, concepts, and roles for the management of IT.
Successful organizations use ITSM to design, create, deliver, operate, manage and improve the IT services that underpin their business activities.
The core concept of ITSM is the belief that IT should be delivered as a service, focusing on meeting customer needs.
What is the Relationship between ITSM, the Service Desk, and Service Requests?
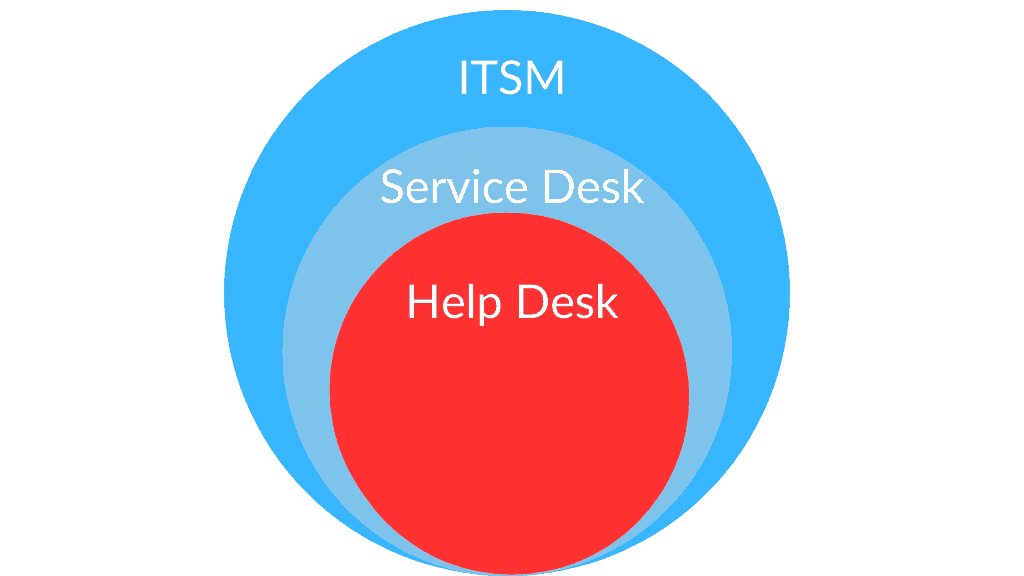
The ITSM framework includes many processes and functions.
The service desk function acts as the main contact point between IT providers and users, handling service requests like information access or equipment needs.
Integrating the desk within wider ITSM is essential for effective IT service delivery.
What is the Goal of IT Service Management
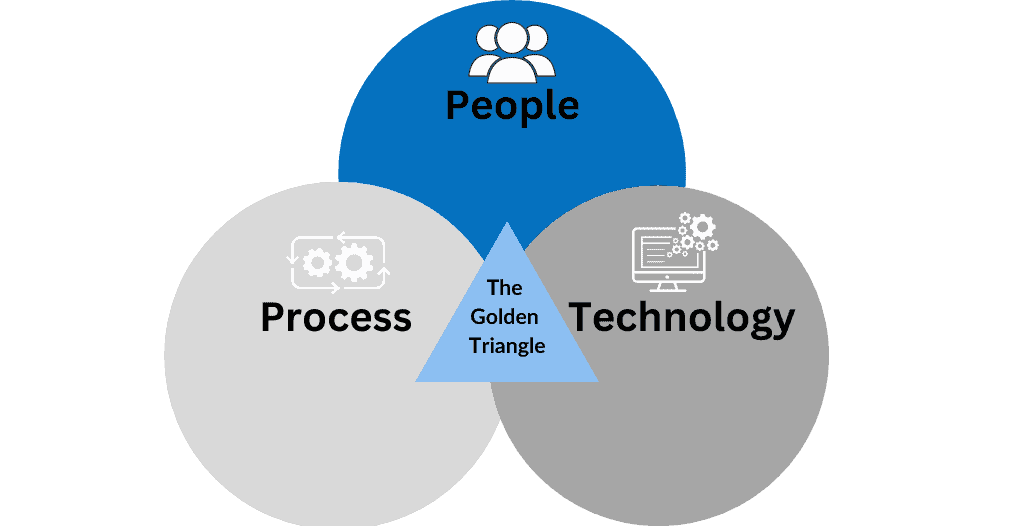
ITSM’s goal is to ensure that the appropriate processes, people, and technology exist in order that the organization can meet its business objectives, using an IT governance framework to manage the full lifecycle of IT services.
What is the difference between ITIL and ITSM?
ITIL was previously an abbreviation for the Information Technology Infrastructure Library.
The framework provides a set of detailed practices for ITSM. These focus on the alignment of IT services with the needs of the business.
There have been several iterations of the ITIL frameworks. The most recent is ITIL 4.
It includes guiding principles, practices, a service value chain, continual improvement, and governance.
ITIL is not the only framework for ITSM, but it is probably the most widely recognized and used.
What other ITSM frameworks are in use?
There are several other ITSM frameworks in use worldwide. Here are two examples:
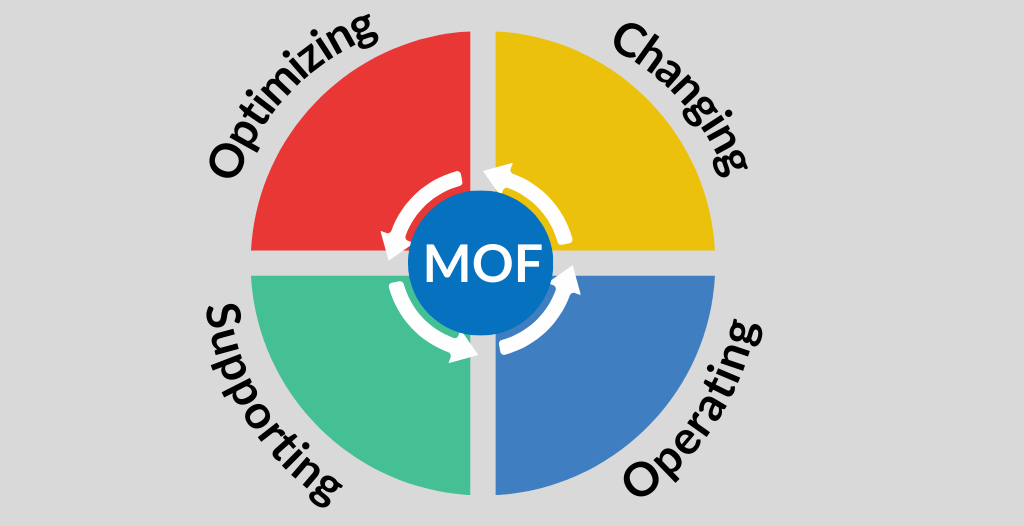
Microsoft Operations Framework (MOF)
This framework helps organizations enhance the reliability, availability, supportability, and manageability of Microsoft technologies and Microsoft products.
MOF’s guidance is designed to support different aspects of managing IT, including challenges related to technology, management, people, and processes.
CoBIT
CoBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) is a framework for IT governance and management that can be used by any IT service provider and for any IT infrastructure.
CoBIT provides guidelines and best practices to help organizations ensure effective and efficient use of IT to achieve their business goals.
It uses control objectives to align IT processes with business objectives, manage risks, optimize resource utilization, and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
2. Understanding ITSM Processes
Processes are the heart of managing IT services. ITSM includes over 30 processes, some are more critical than others.
Deciding which of these processes to implement requires a clear understanding of:
- the goals of the organization
- what processes already exist
- the maturity of those processes
- IT infrastructure
- desired service availability
- current and future information technology services
- the skills of existing staff
- the capabilities and processes of development and operations teams
- and more.

What are the Processes in IT Service Management?
ITSM includes a wide variety of related processes, including:
- incident management
- service request management
- problem management
- change management
- capacity management
- availability management
- service level management
- license management
- configuration management
- service portfolio management
- service catalog management
- asset management
- business relationship management
- self-service
- strategy management
- financial management
- and more.
A typical framework for IT service management groups the ITSM processes into lifecycle stages:
Service Strategy
The lifecycle starts with the Service Strategy stage, where the groundwork for IT organizations is laid.
It includes defining the goals and objectives of IT services, aligning with the business needs, and business processes.
Service Design
The objective of this stage is to design IT services that meet both current and future business needs.
Good service design requires a methodical approach, including defining each service asset, and considering the design of:
- service architecture
- processes
- process management
- agreed service level targets
- supporting tools
- IT organization
- and more.
Service Transition
This phase is about the development, testing, and deployment of IT services into the live environment, ensuring that services and changes are deployed smoothly and integrated effectively with existing services.
Effective service transition is essential to manage the risks of making changes to IT.
Service Operation
The Service Operation phase is where the benefits of the IT services are realized.
This stage is characterized by the day-to-day activities of IT operations teams, handling of service requests, incident resolution, and overall maintenance of live services.
Continual Service Improvement
Continual service improvement stresses the importance of ongoing improvement and optimization of services and processes in all lifecycle stages and for all IT services.
This involves learning from past experiences and making fact-based decisions to enhance service quality continually.
3. Benefits of Implementing ITSM
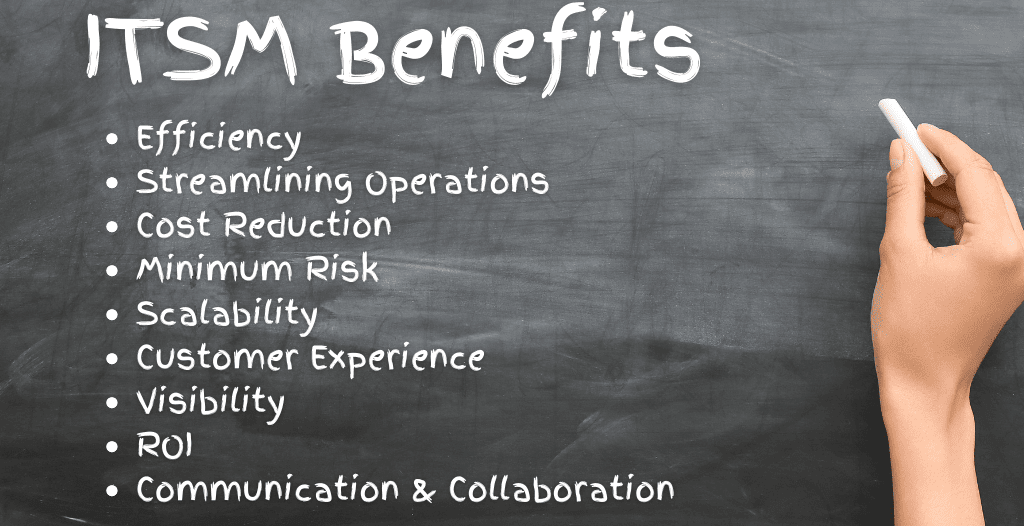
Implementation offers a multitude of benefits that can transform the way organizations manage and deliver IT.
Improved Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of ITSM is the standardization of IT processes, helping to streamline operations, eliminate duplication, and optimize resources.
The automation of routine tasks, facilitated by ITSM software, significantly reduces manual effort, further increasing overall operational efficiency.
Enhanced Service Quality
IT service management includes regular monitoring and evaluation of the performance of the IT services against agreed service level agreements (SLAs) and key performance indicators (KPIs).
Cost Reduction
Implementing ITSM can lead to significant cost savings for organizations.
By optimizing IT processes and resources, reducing downtime, and preventing IT incidents through proactive management, ITSM helps lower operational costs.
ITSM’s approach to problem management helps in identifying and resolving the root causes of issues, preventing costly recurring incidents.
Risk Management
ITSM provides a structured approach to managing risks associated with IT.
The approach includes the identification of potential risks, understanding the possible impact, and creating appropriate countermeasures to mitigate them.
This proactive approach to risk management not only safeguards the IT environment but also ensures business continuity and resilience.
Alignment with Business Goals
Probably the most strategic benefit of ITSM is its ability to align services with the overall goals and objectives of the organization.
ITSM ensures that IT operations and services support the broader business strategy, thus enabling organizations to achieve their goals more effectively.
Facilitating Digital Transformation
ITSM can play a critical role in facilitating digital transformation initiatives.
The framework for the effective management of IT enables organizations to embrace new technologies and digital processes more easily.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
ITSM fosters better collaboration and communication within IT teams and across different departments, using clear processes and defined responsibilities.
This, in turn, leads to improvements in teamwork and more effective cross-functional collaboration.
4. What are ITSM Best Practices?

Using best practices will help you to create an environment that supports and enhances your business.
Typical examples of best practices include these key elements:
Adopt a Framework:
Implement ITSM using established frameworks like ITIL or CoBIT that come with proven processes and methods.
Align with Business Objectives:
Ensuring IT services are in line with the overall business goals and strategies.
Focus on Customer Service:
Prioritizing customer satisfaction and user experience in the delivery of IT services.
Continual Improvement:
Regularly evaluate and improve IT services and processes for efficiency and effectiveness.
Process Standardization:
Standardizing processes to reduce variability, improve predictability, and enhance efficiency.
Effective Change Management:
Managing changes in IT services and infrastructure carefully to minimize impact on business operations.
Incident and Problem Management:
Efficiently resolving incidents and identifying underlying problems to prevent future occurrences.
Knowledge Management:
Maintaining a knowledge base for IT support staff and users to reduce resolution times and improve service quality.
Performance Measurement:
Using metrics and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) to measure the performance and impact of IT services.
Risk Management:
Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to ensure the stability and reliability of IT services.
Resource Management:
Optimizing the use of resources, including people, processes, and technology, for cost-effective service delivery.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs):
Establishing clear and agreed SLAs to set expectations for service delivery and performance.
Training and Development:
Investing in continuous training and development of IT staff to keep up with technological advancements and improve service delivery.
Collaboration and Communication:
Encouraging effective communication and collaboration within the IT team and across the organization.
Utilizing Technology:
Leveraging technology, like ITSM software and automation tools, to enhance service delivery and efficiency.
5. ITSM Tools: What They Are and Top 10 Recommendations
What Is an ITSM tool?
ITSM software tools play a pivotal role in automating and streamlining IT service processes.
ITSM software is essentially a software tool that helps organizations manage IT efficiently, irrespective of which ITSM platforms they use.
Each of these tools offers unique features and pricing models, catering to the diverse needs of different organizations.
When choosing ITSM software, consider factors like the size of your IT infrastructure, the complexity of your IT processes, integration needs, and budget constraints to ensure you choose the tool that best fits your organization.
What are the Top 10 ITSM Software Tools?
Here’s a closer look at the top 10 ITSM software, including key features and typical pricing:
1. ServiceNow

Description: ServiceNow is a widely recognized ITSM software tool that offers a full suite of capabilities.
It’s known for its robust cloud-based platform that integrates various ITSM processes with AI-powered analytics for enhanced decision-making.
Use can also be extended into enterprise service management and project management.
Features: Automated ITSM processes, AI-powered analytics, cloud-based platform.
Pricing: Custom pricing based on the specific needs of the business.
2. Atlassian Jira Service Management

Description: Jira Service Management from Atlassian is a popular tool among in IT for its agile incident management and service request handling.
It provides a versatile platform for managing change and maintaining a configuration management database (CMDB).
Features: Incident management, service request management, change management, CMDB, strong integration with tools for software development and management of hardware and software assets.
Pricing: Offers a free version; Premium version starts at $20 per user/month.
3. BMC Helix ITSM

Description: BMC Helix ITSM stands out for its cognitive automation capabilities and optimization features for service management systems.
It’s particularly effective for businesses operating in multi-cloud environments.
Features: Cognitive automation, service optimization, multi-cloud management.
Pricing: Custom pricing based on requirements.
4. Zendesk

Description: Zendesk is known for its user-friendly interface. It’s a great choice for businesses looking for service desk tools with strong knowledge management integration, and support requests capabilities.
Features: User-friendly IT service desk, self-service portals, knowledge management, integration capabilities.
Pricing: Plans start at $5 per agent/month.
5. Freshservice

Description: Freshservice is ITSM software that supports the core management processes.
It also offers features for the management of assets and analytics.
Features: Incident, problem, change, and release management, hardware and software asset management, and analytics.
Pricing: Starts at $19 per agent/month.
6. Ivanti Service Manager

Description: Ivanti Service Manager is designed for cloud optimization and is ITIL-ready.
It provides workflow automation and self-service capabilities, making it a versatile tool for many teams in IT.
Features: ITIL framework ready, cloud-optimized, workflow automation, self-service capabilities.
Pricing: Contact for a custom quote.
7. ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus

Description: ManageEngine’s ServiceDesk Plus is focused on Information Technology Infrastructure Library processes.
It’s a tool for managing incidents, problems, and changes in IT service processes.
Features: Focus on ITIL processes, incident management, problem management, and change management.
Pricing: Free for up to 5 agents; paid plans start at $10 per technician/month.
8. SolarWinds Service Desk

Description: SolarWinds Service Desk ITSM software is known for its service automation features.
It’s well-suited for organizations needing a tool for risk detection, compliance management, and extensive reporting.
Features: Service automation, risk detection, compliance management, reporting.
Pricing: Starts at $19 per user/month.
9. Cherwell ITSM

Description: Cherwell ITSM offers a highly flexible platform with codeless configuration.
Its automated workflows and dashboard reporting make it a strong contender in the ITSM tool market.
Features: Flexible, codeless configuration, automated workflows, dashboard reporting.
Pricing: Contact for pricing information.
10. SysAid

Description: SysAid excels in automating service requests and managing IT assets.
It also offers performance benchmarking features across many aspects of IT service management.
Features: Automation of requests, management of IT assets, performance benchmarking.
Pricing: Contact for a custom quote.
Real Use Cases of ITSM
To illustrate the practical applications of ITSM processes, here are some example use cases.
They demonstrate the versatility of ITSM in various sectors, highlighting its ability to improve service delivery, satisfaction of customers, and operational efficiency.
Financial Sector
A leading bank implemented ITSM to streamline its incident management process. This led to a 30% reduction in incident resolution time, significantly enhancing customer satisfaction.
Healthcare
A healthcare provider used ITSM for better management of IT assets, leading to improved tracking and maintenance of medical equipment, which enhanced patient care services.
Education
A university adopted ITSM for efficient service request management, enabling students and staff to easily report issues and track the status of their requests, improving the overall educational experience.
Retail
A global retail chain implemented ITSM to manage their IT infrastructure more efficiently, resulting in faster resolution of IT-related issues and enhanced service efficiency in stores.
Telecommunications
A telecom company utilized ITSM for change management, enabling them to manage network updates more effectively, thus ensuring higher network availability and improved customer experience.
7. Challenges and Misconceptions about ITSM
While ITSM offers numerous benefits, organizations often face challenges and misconceptions during its implementation. Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach, involving clear communication, effective training, and a focus on the overall business objectives.
Integration Complexity. Integrating tools with existing systems can be complex, requiring careful planning and execution.
Resistance to Change. Employees may resist new processes and tools, highlighting the need for effective change management strategies.
Cost Concerns. Organizations are often concerned about the costs associated with implementing tools and training staff.
Underestimating the Importance of Training. Adequate training and skill development are crucial for IT teams to leverage ITSM tools effectively.
Conclusion
ITSM plays a pivotal role in aligning IT services with the goals of the business, enhancing service delivery, and retaining satisfied customers.
As technologies continue to evolve, IT service management will remain a critical component for organizations seeking to optimize their IT services and achieve their goals.
By overcoming challenges and dispelling misconceptions, organizations can fully harness the potential of ITSM to drive growth and success.




