Introduction to Service Catalogs and the Service Portfolio
A service catalog is a comprehensive list of services an organization provides or offers to its employees or customers.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe IT Service Catalog is a critical component in IT service management (ITSM), serving as a knowledge base for users who need to understand what services are available, how they can access them, and what they can expect regarding service levels.

Understanding the Role of Service Catalogs
The primary purpose of a service catalog is to improve efficiency, streamline service fulfillment, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Not only does it provide customers or employees a place to discover the services a provider offers, but when moved online, it provides them with a way to log requests for goods and services. It allows the provider to scale the delivery of these services through streamlined fulfillment processes and automation.
The service catalog can offer an excellent customer service experience when complete, well-maintained, and well-designed.
This article explores the service catalog, online service catalog tools, and best practices for catalog design.
The Service Portfolio
The service catalog is part of the service portfolio, which is used to define and document three types of services offered by a provider:

The service pipeline tracks proposed services and their potential value, enabling a business to invest in those services that will grow the organization’s competitive edge.
The service catalog represents active services that end users can use to fulfill their outcomes and drive value to the business. It represents the funding needed to run or operate the organization and include the supporting services operated by IT.
Retired services are documented for their historical value but represent resources that can be recaptured and used for new or operational services.
The Customer-Facing Business Service Catalog
The business service catalog is a portion of the service portfolio that documents active services aligned with the outcomes employees or customers use to create value in their organization.
This catalog delivers value to the business by ensuring that users can easily understand and access services that help them perform their jobs more effectively and that IT is aware of the services supported by technical infrastructure and applications.
The IT-Facing Technical Service Catalog
The technical service catalog is intended for the internal IT team, including detailed technical descriptions of the IT services, including their components and relationships with other services.
Many IT-to-IT requests and repetitive standard changes can be automated through the technical catalog using predefined workflows that include approvals, along with virtual technology and scripting or orchestration.
Service Catalog Importance in IT Service Management (ITSM)
The IT service portfolio and catalog are crucial for effective IT service management, shifting IT to be more services-based, enhancing communication, improving delivery, efficiency, and quality, aiding resource and cost management, and contributing to overall customer satisfaction and strategic alignment.
The service catalog provides an online view of active services in the service portfolio, helping to set the right expectations and improving the overall service delivery process. It supports service request management by displaying the available services, service levels, and costs.
The IT service catalog helps with service request management and customer satisfaction in several ways:
Clarity and Communication
Service Accessibility
Standardization of Services
Efficient Service Delivery
Resource Management
Cost Management
Service Improvement
Compliance and Governance
Customer Satisfaction
Strategic Planning
Key Components of the Service Catalog
Ensuring each service offering in the catalog is clearly defined and documented increases customer satisfaction by providing users with the information they need to log requests.
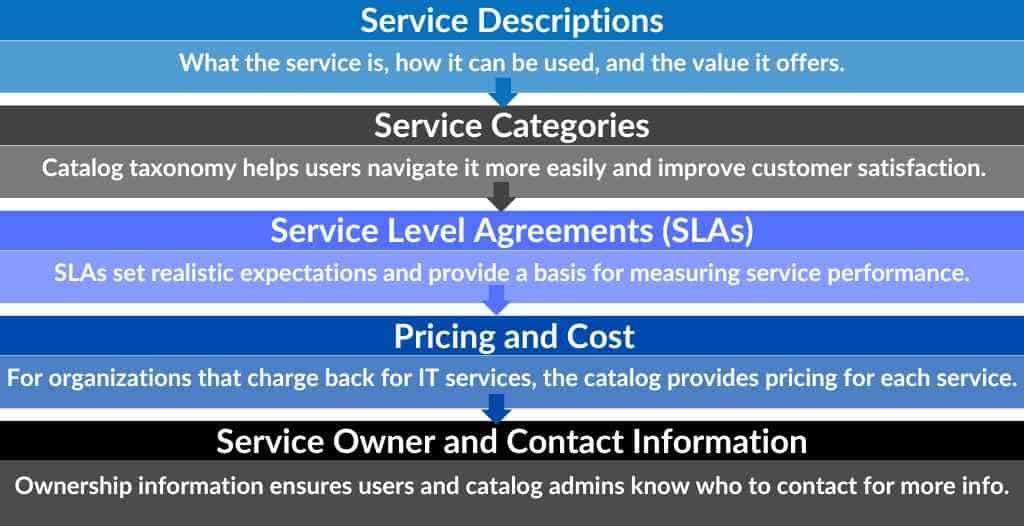
Service Descriptions
A detailed description of service offerings, their use, and their value helps end users understand the available options and make informed decisions about their needs.
Service Categories
Even though users should be able to search a catalog for what they need, creating a taxonomy and organizing the items into categories such as hardware, software, and supplies helps users browse the catalog to see service offerings more easily.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
SLAs define the expected performance and quality of service. They include details about response times, availability, and responsibilities of the service provider and the user. Organizations should create service-specific SLAs to meet these needs.
Pricing and Cost Information
For organizations that chargeback for IT services, the service catalog provides pricing details for each service. This transparency in service costs helps users understand the financial implications of their requests and allows organizations to manage IT budgets more effectively.
Service Owner and Contact Information
While the service desk remains the primary contact for questions and escalations, each service in the catalog should have designated service owners and contact information. This ensures that users and catalog administrators know who to contact to manage and maintain the service listing over time.
Types (and Examples) of Service Catalogs
Numerous IT service management platforms include an integrated service catalog tool, making it easy for organizations to offer service catalogs to their employees and customers.
ServiceNow Service Catalog

Key product features:
Centralized Service Access: The catalog offers a single access point for all enterprise services, including IT services, HR processes and services, legal reviews, and facility requests.
Automated Workflow Management: Automated fulfillment workflow and approvals for fulfilling service requests, including AI and orchestration to automate fulfillment.
Self-Service Options: Users can resolve common issues or fulfill standard requests without engaging the service desk by using automated service requests for true self-service.
Mobile Accessibility: The catalog and knowledge base are accessible via mobile devices, and there are mobile applications for onboarding and IT service and support.
BMC Helix Digital Workplace
BMC Helix Service Catalog is part of a cloud-based integrated IT Service Management (ITSM) suite designed to streamline the delivery and management of IT services within an organization.

Key Product Features:
Service Catalog Functionality: The IT service catalog is a centralized repository where employees can browse and log requests for hardware, software, access permissions, and other IT-related services.
Automation and Integration: BMC Helix integrates with other systems and tools within the ITSM framework to automate the fulfillment of requests.
Self-Service Capabilities: Users can resolve common issues or fulfill standard requests without engaging the service desk by using automated service requests for true self-service.
Mobile Accessibility: The product is accessible via mobile devices.
Ivanti Service Manager
Ivanti service catalog is a feature of its integrated cloud-based ITSM platform designed to streamline the process of managing and delivering IT services within an organization.

Key Product Features:
Centralized Service Catalog: The IT service catalog allows employees to browse and log requests for various IT services using a user-friendly interface that provides access to hardware, access requests, and more.
Automated Workflow: The IT service catalog uses automated workflow to ensure the request is processed efficiently. This includes approval, routing, complex fulfillment processes, and tracking the request’s progress.
Self-Service Portal: Employees can request services, track their requests, find information, and access various IT resources.
Mobile Accessibility: The product is accessible via mobile devices.
Jira Service Management Service Catalog
Jira service management offers a service catalog tool, a cloud or on-premises solution, is designed to help organizations efficiently manage their employee and external customer requests and offerings.

Key Product Features:
Service Request Management: The service catalog allows users to request help, services, or resources from IT, HR, and facilities management.
Workflow Automation: The catalog integrates with Jira’s ITSM platform, allowing for the automation of service request processes and integration with processes like development and change management.
Self-Service: The product includes a knowledge base, allowing users to find answers to common questions and solutions to frequent issues without engaging the service desk.
Mobile Accessibility: The product is accessible via mobile devices.
ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus
ManageEngine’s Service Catalog is a feature within their cloud or on-premises IT service management platform designed to enhance the efficiency of IT service delivery and improve the end-user experience.

Key Product Features
Service Catalog Definition: The IT service catalog is a centralized directory of all the IT services available to the organization’s users, including detailed descriptions of each service, service levels, costs, and processes involved in making them available.
Automated Workflows: Workflow capabilities include routing the request to the appropriate IT personnel, tracking the progress of the request, and ensuring that it is fulfilled promptly.
Self-Service Portal: The Service Catalog is part of a broader self-service portal where users can not only request services but also find information, report issues, and track the status of their requests.
Mobile Accessibility: The catalog is accessible via mobile devices.
Technical and IT Service Catalog Integration with Cloud Services
Many cloud service providers offer catalogs for their customers with detailed listings of their services to help them understand, compare, and manage the vast array of cloud services available, facilitating better decision-making and usage of cloud resources.
Cloud service catalogs enable IT organizations to integrate cloud services into their technical service catalogs, enabling approval and automation of cloud-based solutions.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS allows organizations to offer technical catalogs of their approved AWS services. They offer a connector that enables organizations to include their services in an existing IT service catalog, providing any additional approval workflows needed to manage requests associated with AWS services.

The AWS catalog manages access control for different users, ensures they can only deploy approved services, and provides the ability to customize individual service catalogs for different groups within an organization.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
The Google service catalog helps enterprises to organize, manage, and provision cloud resources on Google Cloud Platform consistently and securely across the organization.

Users can understand and manage cloud resources by grouping them into catalogs, controlling who can access them, and connecting them with projects.
It also allows for managing infrastructure as code and provisioning Google Cloud resources with Terraform.
Microsoft Azure
The Azure service catalog enables Microsoft customers to create, manage, and share Azure services and resources within their technical service catalog. They can also integrate Azure with customer-facing services in the business service catalog, enabling service request automation.

Using the Azure service catalog helps organizations enforce standards and improve governance and compliance by ensuring that only approved resources are used.
Creating and Managing Service Catalogs
Steps to Build a Service Catalog
Building a service catalog involves several key steps:
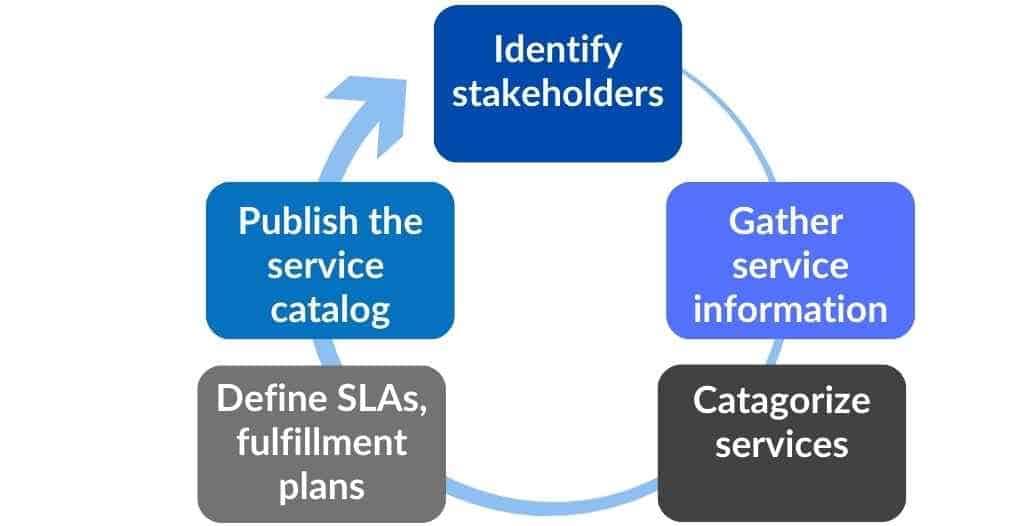
Identify stakeholders: Understand who defines and offers services and who will use the catalog, including customers with access to internal services. The service catalog management team can also designate service owners during this process.
Gather Service Information: Working with key stakeholders, collect detailed information about each service, including descriptions, SLAs, and costs.
Categorize Services: Organize services into logical categories for straightforward navigation.
Define Service Levels: Working with business and IT stakeholders, establish clear and acceptable SLAs for the delivery of each service.
Publish the Catalog: Make the catalog available to users, typically through a self-service portal.
Best Practices in Design and Implementation
Designing an Effective Service Catalog
The concepts below can help organizations avoid common service catalog mistakes:
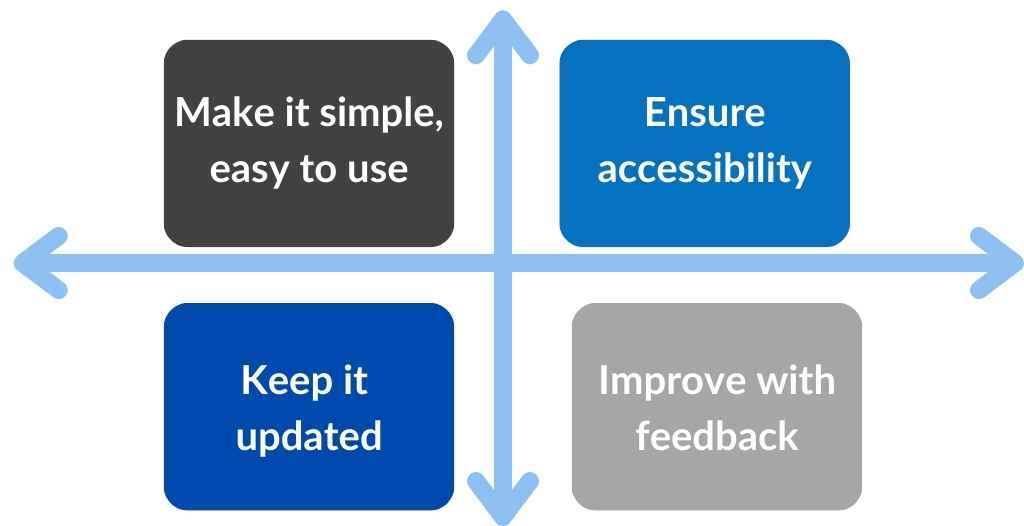
The best catalog is one that is simple and easy to use.
Regular reviews and updates are essential to maintain accurate information.
Make the catalog available on all device types and use accessibility guidelines for colors, fonts, and images.
Collect feedback to improve the catalog design and services offered continuously.
Integrating the IT service catalog with other ITSM processes like incident management, change management, and the CMDB ensures a seamless flow of information and enhances the efficiency of service delivery.
Designing Service Requests
Service request design is key to service catalog adoption, yet common design elements are often overlooked.
Keep forms simple by limiting questions to only those absolutely needed to fulfill the request and which the end user will know.
The end user’s name, contact information, device models, and serial numbers should be available in the system and not needed on the service request form.
Categorize incidents when the ticket reaches the service desk.
Avoid highly technical configuration questions except in the technical service catalog.
If a process is complex, a personal consult may be needed to avoid lengthy and complex forms, keeping the user experience acceptable.
Avoid jargon: All departments use terminology that is familiar to them but not to the end user. Using simple language is more effective than functionally-based jargon.
Service Catalog Management
Service catalog management is a practice concerned with identifying and documenting services and maintaining the accuracy of the catalog. It is part of an overall continual service improvement practice for the catalog.
Service catalog management includes several critical tasks that should be performed routinely:
Auditing the catalog and workflows ensures service request workflows comply with security and corporate policies.
Reviewing catalog contents to ensure the services offered are accurate, including adding new services and removing retired services.
Reporting on and managing service level agreements associated with the services requested.
Use reports to identify the most popular services as well as services that may be retired from the catalog.
Benefits of Implementing a Service Catalog

Improved End User Experience and Service Delivery
A well-designed service catalog makes it easier for users to find and request the services they need, leading to a better overall user experience. Standardizing the request fulfillment process makes service delivery more efficient and consistent.
Enhanced IT Governance and Compliance
With clear service offerings and SLAs, a service catalog helps set expectations and ensure that all IT services are delivered in compliance with organizational policies and standards.
Effective Request Fulfillment
Service catalogs create a one-stop shop that automates the request and fulfillment process, reducing the workload on the IT service desk and streamlining the delivery of services by automating approval and fulfillment workflows.
Cost Management and Resource Optimization
A clear overview of all services and their costs helps organizations manage their IT budgets more effectively, allowing for better resource allocation and utilization.
Security and Compliance in Service Catalogs
Requiring users to log into the service catalog provides the ability to secure access and personalize views, ensuring they can only request services appropriate to their role, while standardized workflows ensure fulfillment of requests occurs in compliance with corporate policies.

An effective service catalog security configuration provides the following benefits:
Protects sensitive data
Ensures offered services remain untampered from creation to delivery
Enhances user and stakeholder confidence in the safety and reliability of IT services.
Additionally, the standardization of items within the service catalog and their fulfillment workflows ensures compliance, enabling organizations to address industry regulations, avoid penalties, and protect their reputation.
Strategies for Ensuring Security and Compliance
Organizations should include strategies for securing and operating a compliant service catalog in their service catalog design process, regularly reviewing the catalog to ensure these needs are met. There are five key areas to consider:
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
Getting catalog design right and driving user adoption can be challenging. Here are some areas to consider:
Design a process to review services, ensuring they remain accurate and up to date.
Create a process to introduce new services into the catalog as they are deployed and to remove retired services.
Find a good balance between standardization and flexibility. Where the opportunity to order non-standard items is available, use longer delivery timeframes to encourage users to order standard items and to ensure sufficient time to ensure compliance with company standards.
User training and adoption campaigns are critical to shifting behaviors that encourage use of the catalog.
Evolution and Current Trends in IT Service Catalog Design
Advancements in technology and changing business needs, driven by the growth in online service catalog platforms, enable organizations to offer dynamic service catalogs, containing a wide range of services based on user roles, preferences, and demand.

Current trends include:
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning for more personalized, efficient service delivery, predicting user needs, including automation and natural language chatbots to assist end users.
Expanding the scope of catalogs beyond IT to encompass a broader range of business services. This evolution into enterprise service management (ESM) broadens the impact and value of service catalogs across the organization.
Making the service catalog available 24×7 by enabling mobile device capabilities.
Embedding the service catalog into a broader service portal enables communication, knowledge, and links to commonly used applications.
Continual Service Improvement and Evolution
As with any IT tool or process, continuous improvement is key. Future service catalogs will likely be more dynamic, with capabilities for real-time updates, user feedback integration, and adaptable structures to accommodate new types of services and changing business needs.




