Customer relationship management or CRM is the sum of all the processes, principles, and practices that an organization uses while interacting with its consumers.
Table of Contents
ToggleThese interactions are both direct and indirect. Direct interactions would include sales and service transactions involving one-to-one contact with customers.
Indirect interactions involve more operational and strategic aspects, such as market predictions or customer behavior analysis.
For any organization that has to deal with users or consumers, customer relation management is a strategy for learning more about those customers’ needs and behavior to enable the organization to develop stronger relationships with them.
The ultimate aim of any CRM system is to enhance the overall customer experience.
A customer relationship management system of principles, practices, and related techniques for implementation must be geared toward creating and delivering positive experiences for the consumer.
These will induce customers to keep using your products and services and allows your business to develop a solid base of satisfied consumers. Effective CRM can also assist in attracting new customers.
Fundamental Principles of CRM
One of the basics of CRM is information gathering. In order to successfully manage customer engagement with your business, it’s necessary to know as much as possible about the consumers themselves, prevailing market conditions, relevant trends, and the aspects of your internal operations that directly affect your customers.
The basic reasoning is straightforward: If you know and understand exactly how your customer behaves, and what they want or expect, you are better able to anticipate and fulfill their demands.
At their heart, CRM systems enable organizations to collect and analyze customer data and harness insights gained from other business intelligence to enable the organization to plan and implement sales and marketing strategies and develop ways of improving relationships and interactions with consumers.
Strictly speaking, this information gathering and analysis can be a manual process – and for many years, this has been the case.
Historically, individual sales or marketing personnel might record their observations on sticky notes, spreadsheets, email messages, or other documents.
Due to the varying amounts of information stored in this manner across an enterprise, organizations often required several dedicated CRM team members to handle each point of contact.
Furthermore, each contact point in the customer management system might require its own database or physical filing system.
These manual methods left a lot of room for omission, lost or damaged data, and human error. CRM executed in this manner often also resulted in slow response times for client or customer service requests, while the time spent managing chaotic data systems left organizations with little time to market their goods or improve the image of their brand.
That was the old days. What is a CRM system in the modern sense? It shouldn’t surprise you to learn that today’s customer relationship management efforts rely a great deal on software and digital technology.

CRM Systems and Technology
If you mention “Customer Relationship Management” to many people these days, they’ll speak to you about it in terms of the technology.
What is the CRM system in this sense? Customer relationship management is often taken to mean the technology companies, software, and systems that help organizations manage their interactions with customers.
We can likewise examine the CRM technology concept by asking some simple questions.
What is a CRM in technology terms? It comprises a set of systems and tools for compiling customer data across different channels or points of contact that take place between brands and consumers.
These may include visits to company websites, phone calls, email, direct mail, social media, live chat, or promotional materials.
What are CRM systems? These are now generally software-based platforms that give customer-facing business personnel detailed information on consumers.
This data may include buying habits, pain points, past transactions, personal information, and demographics.
A CRM system may be developed by an organization in-house, bought off the shelf, customized from an existing application, or provided as a service by a cloud provider.
What is CRM software? These applications aggregate customer and related information in a single place to give businesses easy access to this data.
The software will typically include tools that enable sales, marketing, and customer service staff to anticipate customer demands, interact with consumers, update transaction and other records, and track performance indicators and goals.
What is CRM system automation? Many customer relationship management platforms offer tools for automating routine sales and marketing functions and customer service delivery processes.
These save organizations much time and effort and help ensure consistency in how they deal with their consumers.
What’s a CRM cloud solution? Customer relationship management tools and services can be made available to businesses on a per-user basis — typically via a monthly subscription.
They provide a range of enterprise-level features and are highly customizable and scalable. Cloud-based CRM systems provide real-time access to their users via any device with an internet connection.
Sales, marketing, and customer service personnel can use them on the road, via their smartphones, or while working from home.
Why CRM Matters to Your Business?
In an economy where the desires and expectations of consumers are paramount to commercial success, the importance of CRM or Customer Relationship Management really cannot be over-stressed.
For organizations in every sector that must regularly deal with users or consumers, Customer Relationship Management is a strategic approach to managing all interactions and dealings with both existing customers and potential ones.
Part of the strategic importance of CRM is that it enables organizations to focus on their relationships with individual people – whether those people be customers, service users, business partners, or suppliers.
The Importance of CRM For Customer Retention
One of the basic tenets of commercial business wisdom is that it costs significantly more to get new customers than it does to retain your existing ones.
Understanding how your customers behave, what they want, and how conditions in the market may change what they expect in the future are key factors in enabling you to anticipate their needs and fulfill their desires while providing the kinds of service and experiences that they value.
And achieving all of this is critical in inducing customers to remain on the books and loyal to your brand.
One of the principal reasons you need a CRM system to enable customer retention is that it brings information together from throughout your enterprise to give you a holistic 360-degree view of each customer in real-time.
This enables your customer-facing employees in areas such as sales, marketing, and customer support to make swift, data-driven decisions that can improve the quality of your sales and marketing efforts as well as your interaction with consumers and your delivery of assistance and services.
These aren’t just nebulous concepts. The importance of relationship management is quantifiable. To illustrate, market research figures from the first quarter of 2021 indicate that 86% of consumers are willing to pay more for the kind of improved customer experience that CRM makes possible.
One in three customers will leave a brand they love after just one negative experience. Customer-centric organizations – the kind that take CRM seriously and put the customer first — are 60% more profitable than those who don’t put the consumer at the center of whatever they do.
CRM Solutions
The use of CRM in business currently represents the major strategic and infrastructure investment for enterprise operations.
In fact, in 2021, revenues from Customer Relationship Management solutions have overtaken database management systems to become the largest of all software markets.
What is a CRM system used for? Customer relationship management systems enable organizations that have to deal with consumers or service users to optimize their sales and marketing efforts with different demographics and customer groups.
CRM data gathering and information management give deeper insights into consumer behavior and desires, helping organizations to improve the way they present and promote their portfolio of products or services.
CRM systems and practices empower organizations to sustain a customer-centric emphasis in their operations and provide 360-degree visibility and a holistic view of their entire relationship with consumers.
In an on-demand economy where the customer rules, this can be critical in providing businesses with the ability to deliver service and support levels that keep them competitive.

CRM Systems Operations
How do CRMs work? There are customer relationship management systems and software for various use cases that provide different tools, but certain principles and functionality are common to all of them.
CRM solutions for business support a customer-centric approach by centralizing all sales, marketing, and customer service information in a single repository – a central database that eliminates the tendency for vital information to be hoarded or forgotten in separate departmental silos.
Easy access to this data across the enterprise enables organizations to develop a complete view of their customers.
By analyzing information in the CRM database, businesses can monitor, manage, and track the performance of their sales, marketing, and customer support activities — often in real-time.
Mapping these activities directly to the consumer enables organizations to enhance the customer experience.
Another aspect of how CRM helps in business operation is through the automation of repetitive tasks.
For example, lead management automation features help marketing professionals identify, qualify, follow up, and eventually convert prospects into actual sales and apply across the multiple channels that prospective customers use to engage with a brand.
Automation tools for customer support can define and implement rules for how different consumer categories are directed to different customer service avenues, with the CRM system automating the entire workflow.
Real-world Applications
What are CRM tools used for in the real world? In essence, there are three main types of CRM for commercial applications.
CRM systems for marketing provide tools for collecting and analyzing data on existing and potential customers across the various channels that consumers use to interact with a brand.
The tools enable marketers to identify trends in customer behavior, buying patterns, and relevant market intelligence.
With this analysis, they can target prospects more accurately and craft personalized and engaging experiences for their customers.
Sales CRM tools put their emphasis on tracking leads and closing deals and provide features to enable sales agents to attract and engage potential buyers and nurture relationships with them on the route to a sale.
As well as providing a central hub for information and task management, CRM systems for sales also provide tools for delivering quotes, tracking sales performance, and organizing sales-related activities.
Customer support CRM solutions provide interactive tools for dealing with complaints and queries, problem resolution, and follow-up activities.
These will typically include a ticketing system and central database for keeping track of individual support cases.
CRM Use Cases for Business
Customer Relationship Management or CRM has a very high profile in the commercial sphere. But why use CRM?
Well, with a CRM platform, it’s possible to work proactively with business contacts, target select audiences, and consumers, track individual leads or customer activity, and nurture relationships with your customers and value chain partners.
In addition, a CRM system provides a centralized access point for personnel across all departments of an enterprise, giving customer-facing staff the information and tools they require to create and sustain engaging and personalized customer experiences.
Functions of a CRM
An easy to use CRM system should provide the tools and features necessary to gain a full and holistic view of the consumer and maintain a customer-centric focus for the enterprise.
These features should cover a number of basic functions, including:
Dashboards to easily visualize your data: An intuitive and well-configured dashboard provides each user with quick access to the information that’s most relevant to their job. Workers should be able to customize this presentation to suit their particular workflow.
Data that enables proactive outreach: Information that’s available to customer service, sales, or marketing personnel can enable these agents to reach out to individual consumers in response to their activities. Such actions can be instrumental in preventing a dissatisfied customer from abandoning your brand or in tipping the balance between a prospect and an actual sale.
Automation tools: These may be configured for repetitive tasks, freeing workers up to concentrate on more high-value or strategic activities. Automation can also extend to specific tasks within a sales funnel or customer support activity chain. For example, a CRM automation routine could be set up to perform a certain function, such as sending a promotional email, in response to a trigger generated by customer activity.
Reliable reports: A CRM system’s reporting tools can give your workers the full picture of who interacts with your brand and how they’re interacting. These reports can provide actionable information to enable your agents to communicate more effectively with your existing customers and reach out to prospective clients.
Collaboration: Many CRM systems (especially those based in the cloud) provide a shared platform for collaborative work and input. This helps reduce the “silo mentality” of information hoarding and enables cross-functional teams to work from the same page.

Using CRM technology
These days, Customer Relationship Management is pretty much synonymous with the software and systems that facilitate it.
Here’s a simple guide on how to use CRM software:
- Register your workers on the CRM platform: When adding users to the system, you’ll need to sell the benefits of using the software — how it will help your sales and marketing people to generate more business, etc.
- Customize the program settings: Your CRM system should have configuration controls for all the various stages of each function, such as the sales progression from lead, to prospect, to customer.
- Import all relevant information to the CRM platform: You may, for example, have CRM information sitting in external spreadsheets.
- Activate any integration with your existing business tools: This will enable you to centralize all your sales, marketing, and customer interaction data and call on the most appropriate tool for each operation.
- Set up your dashboard: This will act as your easy-to-read, central command console.
- Enable automatic reporting: CRM reporting tools enable you to schedule regular feedback on your various activities, with automation leaving workers free to pursue higher-value activities.
These steps apply to dedicated CRM software, but it’s possible to adapt existing tools for customer relationship management purposes.
As an example, if you’re using Outlook as a CRM, you can enter customer contact information, notes, activities, and other data into the contact section of Microsoft Outlook with Business Contact Manager.
Business Use Cases for CRM
In the commercial sphere, there are several CRM uses and use cases – Sales – Support – partner management, to name a few.
For Sales, CRM enables teams to look for prospects at scale through the automation of key sales process areas.
A CRM database allows for the mass importation of contact details, often with tools for automatically converting email addresses into contacts.
Marketing automation tools of CRM can use the centralized customer details, analytics, and insights, to facilitate sales outreach activities.
In the area of Support, a small number of customers with complaints often take up a disproportionate amount of service staff time.
With the 360-degree view of customer activity possible with a CRM system (including past interactions, common service issues, and resolution rates), businesses can identify their “problem” customers and the most efficient and satisfying ways of dealing with them.
The central database of a CRM system can hold not only information on consumers, but also data concerning a brand’s value chain partners, including vendor price levels, and the real-time status of lines of supply.
With tools for collaboration and communication, a CRM platform is therefore also viable as a vehicle for partner management.
The Benefits of CRM
As implied by its name, one of the core benefits of customer relationship management is that it enables organizations to manage their interactions with consumers and nurture and sustain relationships.
This can be instrumental in retaining a solid base of existing customers (and therefore recurring revenue) and developing strategies for attracting new ones.
There are several other advantages of CRM, which include:
Creating More Effective Sales and Marketing Campaigns
Customer relationship management involves the gathering and centralizing of information relating to all aspects of the customer journey and all interactions between a brand and its consumers.
Coupled with analysis of this data, CRM enables sales and marketing teams to create more effective campaigns by targeting potential leads or existing customers with tailored content specifically for them.
Increasing Customer Engagement
Another of the benefits of CRM is its ability to shed light on the preferences and behavior patterns of both individual consumers and specific market segments.
This gives marketers the information they need to create experiences that speak directly to customers, both personally and on a qualitative level.
Consistency Across the Board
One of the benefits of CRM system implementation is that it provides a centralized and common information store for the enterprise.
This allows workers in all departments to retain consistency in branding and how they communicate the organization’s identity to consumers.
Better Service Delivery
Facilitation and automation for customer service and support are two of the benefits of CRM software.
CRM systems give customer service representatives access to all available information relating to support issues and automatically route service requests to the person who is best qualified to handle them. This helps in quickly solving customer issues.
Cost Reductions
One of the CRM benefits for business is its ability to reduce costs and conserve resources. With automation and centralization key to the functioning of a CRM system, these features can save organizations time and money on information management while freeing up skilled sales, marketing, and support personnel to devote their time and energy to more high-value pursuits.
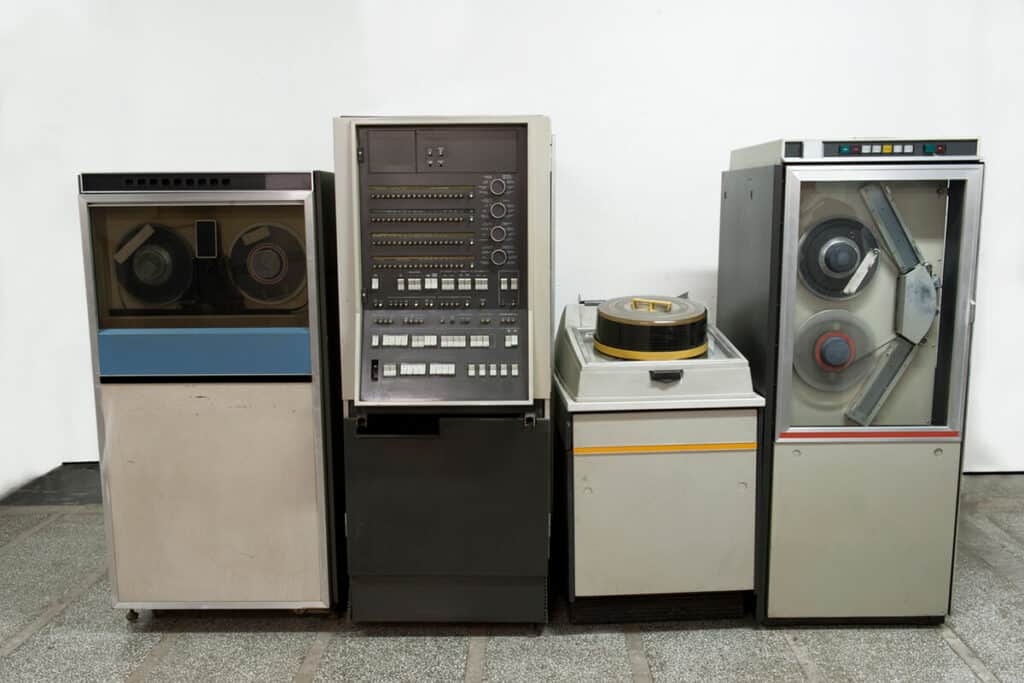

CRM Evolution
The path of CRM evolution begins back in the days leading to the early to mid-twentieth century when businesses used pen or pencil and paper to record their daily activities.
As office furniture developed, businesses made bulk purchases of filing cabinets to house the increasing volumes of handwritten records and documentation.
In 1956, the first rolling index or Rolodex was invented by Danish engineer Hildaur Neilsen. This enabled business users to store contact information and sales prospects in a more portable format.
Customer Relationship Management during the 1960s was very much a hands-on and feet-on-the-ground affair.
Outreach to customers typically took the form of in-person meetings, while sales missions typically took place on a door-to-door basis or via cold calling.
Mainframe computers entered the picture in the 1970s, enabling businesses to register customer information like names, addresses, and transaction histories in a standalone database.
This was also when rudimentary database marketing took off, as businesses used their accumulated information to craft custom messages and monitor the progress of their campaigns on the mainframe screen.
The evolution of CRM took a quantum step in the 1980s, as digital technology made a great leap forward with the introduction of the personal computer or PC.
This ushered in a new age of database marketing, with more advanced information analysis and customized communications.
At this time, too, the handheld data management market made advances, with the launch in 1987 of a digital version of the Rolodex called ACT! by Conductor Software.
ACT! had an in-built contact management tool and paved the way for the development of the first Content Management System or CMS prototypes.

The evolution of CRM software as we know it accelerated during the 1990s. This decade saw the transition of database marketing into Sales Force Automation; with the addition of features like task automation, tracking, and customer data analysis, the benefits of salesforce automation soon became apparent.
In 1995, the term “CRM” was coined, and in 1999 the first mobile CRM (Siebel Sales Handheld) came onto the market.
The salesforce advantage took off when they launched the first cloud-based CRM as a Software as a Service (SaaS) offering.
During the early 2000s, CRM evolved to incorporate enterprise-wide interactions and processes within a single platform. In 2004, SugarCRM released the first-ever open-source CRM system.
The 2010s saw the increasing popularity of mobile CRM solutions and the growing influence of cloud CRM.
Together with big data technologies, this saw customer relationship management capabilities extending to businesses of all types and sizes.
The 2020s are witnessing the rise of social CRM and the increasing use of artificial intelligence or AI in CRM applications.
The Future of CRM
In a previous section, we alluded to how artificial intelligence or AI is beginning to assume a role in the “Future of CRM” outlook for years to come.
For CRM systems, this is likely, to begin with, improved methods of data ingestion and retrieval.
Under current manual input methods, sales professionals spend around 17% of their time entering data into CRM systems, which is roughly the equivalent of one working day each week.
With artificial intelligence, data entry can be both smart and automated, taking in information from a multiplicity of sources and customer interaction channels.
AI-powered techniques such as sentiment analysis are also set to play a role in the future of CRM technology.
Using sentiment analysis, AI-powered tools can analyze conversations with consumers and assess their emotional state in real-time.
Spot analysis of customer interactions with sales or support staff may in the future enable these agents to proactively redirect the course of any conversation.
Artificial intelligence may also figure largely in the future of CRM software implementations, particularly data integrity.
Data assessment tools powered by artificial intelligence can detect anomalies, irregularities, duplicates, and other errors that may compromise CRM information.
AI Integration with third-party data sources may also enable CRM software users to interpolate missing records and update information in real-time, as contact details and other customer or campaign-related information alter.
Some future trends in CRM to watch besides AI include:
The Lowering of Barriers to CRM Adoption
CRM solutions are continuing to reduce in price, especially with cloud-hosted Software as a Service (SaaS) options offering affordable packages to small and medium-sized enterprises. This is likely to increase the level of CRM adoption in the coming years.
The Rise of Social CRM
The COVID-19 pandemic has precipitated a surge in social commerce — the use of social media platforms as sales venues and practices such as group buying to achieve discounts on goods and services.
This represents a growth opportunity for sales, marketing, and customer service delivery. The future of CRM will likely involve the continued integration of social media channels into Customer Relationship Management platforms.
Integrating Voice and Conversational Commerce With CRM
Voice technology is already playing a part in making Software as a Service (SaaS) tools more accessible and easy to use.
In the coming years, we can expect this influence to extend to customer relationship management applications.
Technologies like the Salesforce Einstein Voice Assistant are already making it easier for sales agents to track customer information and message, update, and notify their teams about changes occurring in sales pipelines.
Integrating CRM With IoT
With the Internet of Things or IoT technologies, organizations can closely monitor how consumers interact with their products and services, with feedback and observations in real-time.
Coupled with Customer Relationship Management techniques and technology, this information provides a wide scope for improving the customer experience and extending proactive support in handling customer issues.





