Here’s a saying you’ve no doubt heard, and probably even repeated yourself in recent years: “Today, data is the fuel that drives business success.” But how true is that statement? Well, it is true. Data is the fuel that drives business success – but only so far as the fuel you use to power your business engine is clean and good. Using dirty or bad data to fuel your business initiatives is just like filling your gasoline car with diesel – you think you’re powered up and ready to go, when in fact all you’re doing is causing serious damage to your engine.
Table of Contents
ToggleBad Data
The fact of the matter is that not all data is created equal. There is good data and there is bad data – and the costs of fueling up on garbage can be astronomical. One famous example from history is the Mars Planet Orbiter – a robotic space probe manufactured by Lockheed Martin and launched by NASA in December 1998. The mission was to learn more about Mars, its climate, atmosphere, and surface conditions – but one piece of bad data caused the probe to fire its thrusters incorrectly. The problem was that one piece of software supplied by Lockheed Martin calculated the force the thrusters needed to exert in pounds of force – but a second piece of software, supplied by NASA, took in the data assuming it was in the metric unit, newtons. This resulted in the craft dipping 105 miles closer to the planet than expected – causing its total incineration, setting NASA years back in its quest to learn more about Mars, and a $327.6 million mission being burnt up in space.
Whoops!
But it’s not just astronautics companies that have been guilty of fueling engines with bad data. In fact, it’s quite a common problem. 60% of companies have an overall data health that’s “unreliable”, according to recent research, while 62% rely on marketing and prospect data that’s up to 40% inaccurate.
(Image source: blog.zoominfo.com)
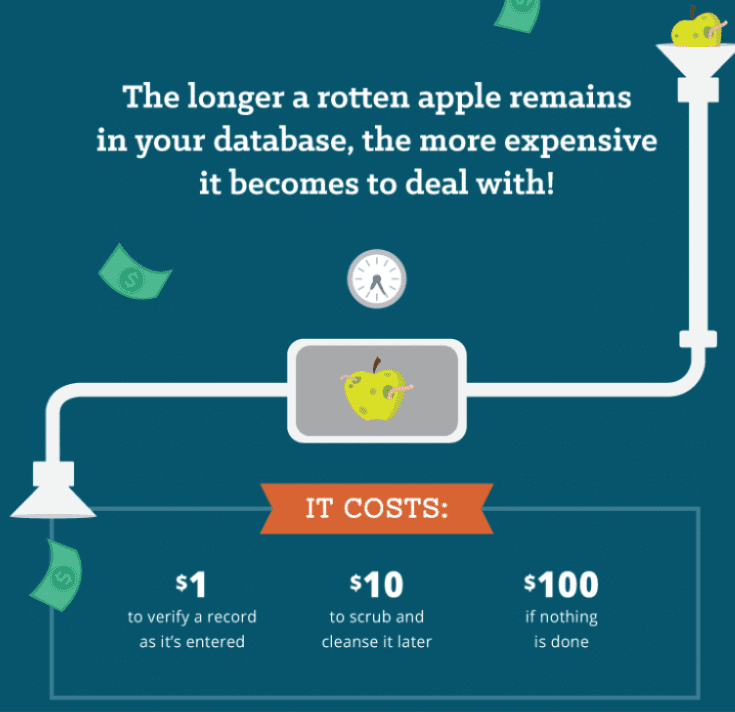
40% inaccurate!! No wonder bad data is costing organizations so much. For starters, 40% of business objectives fail due to inaccurate data (there’s a link between these figures – I just can’t quite put my finger on it). Then there’s the cost of data hygiene – it costs $1 to verify a record as it’s entered into a database, $10 to scrub and cleanse it later, and $100 if nothing is done. As such, 50% of IT budgets are spent on data rehabilitation, with research from IBM revealing that bad data costs US companies over $3.1 trillion a year.

(Image source: ibmbigdatahub.com)
Preventing GIGO (Garbage In, Garbage Out)
Today, data is the new gold rush for businesses, driving more business and marketing decisions than ever before. Everything from content marketing strategies to distribution models rely heavily on data to drive decision-making. What’s more, in the digital age, companies are now brimming with technology. Mobile apps, CRM systems, ERP systems, IoT, enterprise SaaS applications, the cloud – the average medium- to large-size enterprise now has anywhere between 300 and 500 technology investments in place, most of which are producing their own datasets.
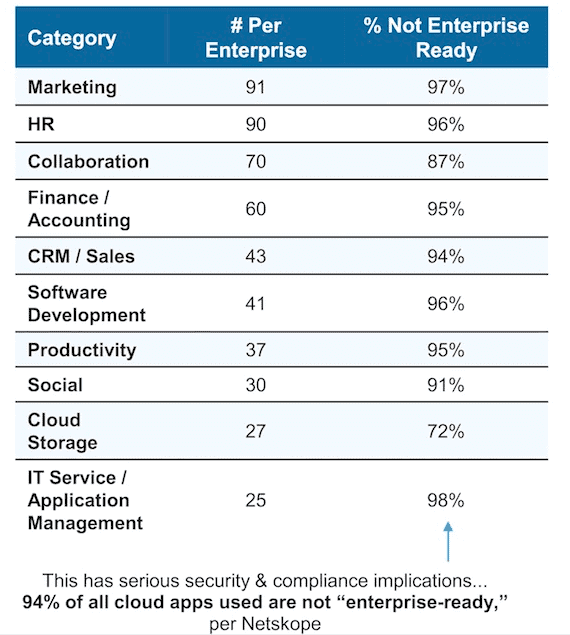
(Image source: chiefmartec.com)
These datasets are used for reporting using business intelligence (BI) tools – and the reporting itself used to gain an overview of the business and make “informed” decisions. However, if bad data is being fed in, then the reporting is going to be inaccurate or incomplete. As such, if your reporting and data analysis is wrong, then your decision-making is going to be flawed, too.
This is what’s known as garbage in, garbage out – or GIGO. If you fuel your business engines with bad data, then, much like the Mars Planet Orbiter, it won’t be long until you crash and burn.
GIGO is the root cause of many ineffective – if not outright disastrous – marketing campaigns. Today, with dynamic websites, social media, email, and multiple other channels at its disposal, marketing relies on an ability to bring together first-, second- and third-party audience data to accurately target individuals with relevant content and personalized experiences. However, if that audience data is inaccurate, then marketing will be routinely customizing messages in embarrassingly off-target ways – and spending money on campaigns that are targeting the wrong individuals.
Lead databases are extremely prone to GIGO. Invalid, false, or duplicate entries in data fields from prospects – including names, emails, addresses, company info, etc. – all amount to bad data flowing through your systems, inaccurate reporting, and bad decisions being made. This false or misleading data causes marketing to mis-identify and/or improperly quantify lead scores. And if any machine learning algorithms are in play in a CRM or other marketing automation system, then they will be considering bad data in their pattern-matching routines – and useless results will proliferate. Data validation and email validation services can be used to mitigate these issues.
Web analytics tools like Google Analytics that allow organizations to track how a website is generally performing – page visits, bounce rates, social media referrals, clicks, conversions, etc. – also need to be configured properly and implemented correctly with accurate site tagging. In addition, channel platforms – such as your ad server, bid management, marketing automation, SEO, and community management platforms – require advanced configuration, as well as a structured approach to tagging campaign URLs in order to ensure that accurate and complete data is generated and prepared for data warehousing.
Another source of bad data comes from an inability to tie cross-platform customer data together to create a single customer record. Full-featured data management platforms like Actian DataConnect provide a robust solution to GIGO in this regard. Aggregating and segmenting audience data and feeding that data back to paid media, email, and content management platforms for accurate real-time reporting, targeting and personalization, Actian DataConnect provides de-duplication and merging of customer touchpoint data into a single customer record.

“A true 360-degree view of your customers can’t be sourced from a single system, it must be aggregated from many different sources,” writes Actian. “Traditional CRM and data warehouse systems just couldn’t handle all the data sources available, and developing a complex set of integrations was both costly and time consuming.” Writes John Bard, senior director of marketing. “Actian provides a complete solution to enable marketing success. Employ advanced data modeling to de-duplicate, identify common characteristics and create customer clusters that depict the complete picture of your customers’ purchasing habits and preferences.”
Final Thoughts
Bad data hurts businesses. While most organizations today are positively drowning in data, too often, it’s a case of garbage in, garbage out, leading to inaccurate reporting, poor decision-making, and bad results. There’s big responsibility when dealing with big data. Only by keeping bad data away from your business engines will you be able to keep your rocket ship on course with accurate analytics and genuine insights fueling your business decisions.
Bad Data
The fact of the matter is that not all data is created equal. There is good data and there is bad data – and the costs of fueling up on garbage can be astronomical. 60% of companies have an overall data health that’s “unreliable”, according to recent research, while 62% rely on marketing and prospect data that’s up to 40% inaccurate. Then there’s the cost of data hygiene – it costs $1 to verify a record as it’s entered into a database, $10 to scrub and cleanse it later, and $100 if nothing is done. As such, 50% of IT budgets are spent on data rehabilitation, with research from IBM revealing that bad data costs US companies over $3.1 trillion a year. One source of bad data comes from an inability to tie cross-platform customer data together to create a single customer record.





