Human resource planning enables businesses to meet their current and future demands for talent, allowing human resource managers to anticipate and develop the skills most valuable to an organization, and providing the enterprise with the optimal balance of staff in terms of available skill sets and numbers of personnel.
Table of Contents
ToggleIn addition to the immediate advantages, proper planning provides a path for future development by establishing a reservoir of talent capable of filling leadership roles. n the long term, human resource planning helps align human capital management more closely with business strategy.
Did you know?
HR statistics in the US suggest that an alarming number of companies lose $550 billion annually due to workers feeling dissatisfied or disengaged.
Wise businesses, therefore, lay greater emphasis on building a healthy organizational structure that motivates the workforce. This includes promoting healthy communication between management and employees.
In the words of Darrin Murriner, the author of Corporate Bravery, a field guide for eliminating fear-based decisions, and Co-founder of Cloverleaf.me, an HR technology platform, “Human resource planning and organizational strategy connect at the hip. You can’t deliver a business strategy without making sure you have the right human capital you need in the right places for the task at hand.”
With that, let’s dig into the details of Human Resource Planning.
What Is Human Resource Planning?
Human resource planning definition is simple. At its core, Human resource planning is a systematic and strategic process aimed at evaluating the current state of an organization’s human resources and predicting its future workforce requirements.
HR planning, which is also known as workforce planning, helps organizations recruit, retain, and optimize the deployment of people they require to meet strategic business objectives and respond to changes in the market and the general environment.
Beyond a simple consideration as the workforce, the human resources of an organization represent the sum of knowledge, skills, aptitude, creative abilities, and talents available to the enterprise, in addition to the values, attitudes, and benefits that each individual contributes to the business.
A key part of human resource planning is projecting future workforce requirements and developing strategies for managing talent in such a way that it proactively prevents skill shortages or surpluses.
The need for human resource planning is to maintain the balance of skills based on the needs and objectives of the enterprise. HR planning must, therefore, be a continuous process, with a structure and monitoring system that enables the organization to provide sufficient lead time for the recruitment and training of employees.

HR Planning Methodology: Steps in Human Resource Planning
While forecasting workforce demand is at the heart of human resource planning, HR professionals require a comprehensive and in-depth view of their organization and an understanding of multiple factors to put together a plan.
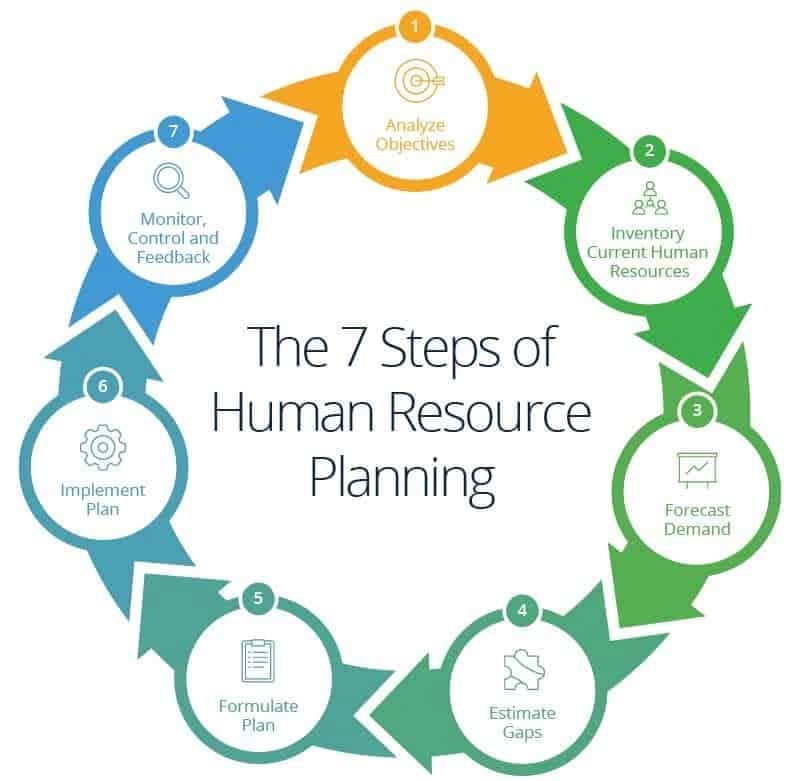
Smartsheet.com identifies seven key steps in the planning process, which may be applied in terms of their relevance to the circumstances of a specific enterprise:
- Analyze the objectives of your organization: the human resource planning is done based on the organization’s goals and objectives, so, it’s important to develop a deep understanding of that.
- Make an inventory of current human resources: Get to know your current workforce; their skills, competencies and experiences. Also, try to identify their strengths and weaknesses.
- Forecast your HR demand: Sketch out potential workforce requirements based on your organization’s objectives and plan.
- Determine the number and extent of skills gaps: Compare the projected requirements and determine the extent of skill gaps.
- Draw up an action plan: Solve the gaps through recruitment, training and development.
- Integrate and implement the plan: Collaborate with the required departments to execute your action plan.
- Monitor, measure, and provide feedback: Monitor the outcomes and keep track of the progress. Based on the results, provide feedback and improvise.
(Image source: Smartsheet.com)
If you wish to understand these steps in detail, read our previous blog: ‘What Is Human Resource Planning?’.
The Implications and Benefits of Human Resource Planning
In a globalized economy fueled by technological innovation, constantly evolving work patterns, demographic or cultural shifts, and changes in customer behavior, the life cycles of business designs and products are shortening – and organizations must be able to adapt swiftly.
In this regard, human capital is more flexible than physical infrastructure or finance. Therefore, businesses must take into account human resource planning as a vital element required to survive and thrive.
Organizations around the world are recognizing the importance of this. For example, 2020 HR statistics reveal that 89% of medium-to-large companies have started using comprehensive annual surveys for engagement assessment.
These studies are assisting them in understanding their workforce better and learning how to keep employees motivated and productive.
Businesses are also appreciating the importance of making a good first impression on their prospective employees and providing an incentive for them to fit into the organization and work enthusiastically for its success.
Human resources statistics from 2019 indicate that 87% of applicants make a positive evaluation of the company and position they’re applying to, after a positive interview and onboarding experience.
The reverse also holds, with 83% of applicants who reported a negative interview experience changing their initially positive opinion about the company and the position they’re applying to.
Moving forward, human resource planners will not only have to face the adoption of new digital processes and technologies — they will also have to accommodate new methods of doing business, and new realities such as the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, with its movement restrictions and emphasis on remote working and collaboration.
They will likely have to develop new methodologies for nurturing and retaining existing skills and cast a broader net in discovering new talent.
Matthew Burr, Moderator of the Upstate HR Podcast and Principal at human resource consulting firm Burr Consulting, LLC, sums it up like this:
“The war for talent around the world continues to grow. To win the human capital competition, companies should use a strategic human resource plan as a roadmap to achieve three- to five-year goals. Strategic plans influence the development of tactical resource planning.
For example, a human resources strategic plan may include long-term aims to recruit and retain excellent staff with a high level of technical expertise. The tactical plan would include detailed action plans with completion due dates.
For the strategic recruitment goals, the tactical program might consist of short-term goals, such as benchmarking salaries via survey data, or creating a social media campaign to identify and recruit technical professionals. The plan may also target filling IT positions through international recruiting.”

Importance of Human Resource Planning: What it Brings to the Organization
When executed effectively, HR planning enables businesses to optimize their usage of human resources, increasing productivity while reducing labour turnover, employee unrest, and absenteeism.
It’s important to the enterprise in several respects.
The five business management functions including planning, organizing, leading, directing, and controlling rely on the oversight and action of human resource planners
At the organizational level, good HR planning enables the enterprise to optimize its deployment and utilization of available talent and project the need for additional or alternative skills well in advance
Besides optimizing its usage of skills, the planning function also provides the organization with a clearer path to the future, both in terms of anticipating skills requirements and creating an order of succession for the promotion and shifting of talent within the corporate hierarchy.
Strategic workforce planning enables managers to more easily adapt to changes when employees retire or leave the organization, and when it comes time to promote or transfer personnel.
In times of economic uncertainty, human resource planning becomes a value add for the organization, with its power to foresee and avoid short-sighted staffing decisions.
For example, unnecessary downsizing may result in costs to the enterprise and possibly, backlash from worker’s unions. Also, replacing these employees will cost time, effort, expense, and training.
On the employee front, a comprehensive,well-executed HR plan can provide improved communications with management and a greater connection with the vision and objectives of the enterprise.
A human resources scheme with provision for incentives can also increase the worker’s engagement with the organization, their commitment to its progress, and their sense of job satisfaction.
Challenges Faced in Human Resource Planning
Predicting workforce requirements is not the only challenge human resource professionals are left to face. Below are some common challenges HR professionals need to overcome on a regular basis.
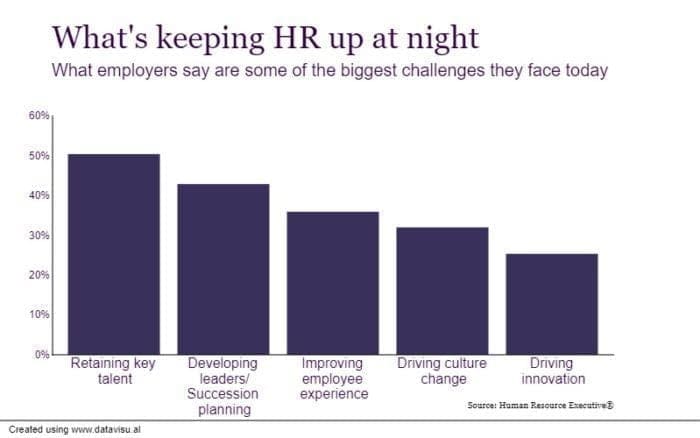
(Image source: Human Resource Executive)
Change Management: change management is an integral requirement for any human resource planning scheme. Resistance to the process may come from workers who feel that their workload will increase as a result of the implementation, or from those who feel uncomfortable with changes to their working patterns and established routines.
External Factors: fluctuations in market conditions, employee turnover, seasonal employment, absenteeism, and the effects of new technology, may also play a part in complicating matters for Human Resource Planning process
Technical Advancement and Issues: Although 2020 HR statistics suggest that 70% of companies use data analytics to process their employment data, IT and HR managers need to ensure that those human resource information systems are reliable, comprehensive, and up to date. This requires them to keep a close eye on data integrity, management, and in the era of intense privacy legislation, security protection.
Legal Issues: Legal and regulatory compliance requirements can form an obstacle to effective HR planning in themselves. In the US, for example, the processes and documents that employers use for recruiting, interviewing, and staffing may have different requirements or injunctions from state to state.
Many states passed new harassment prevention laws in response to the “Me Too” and “Time’s Up” movements, organizations must take account of their own status with regard to their obligations for mandatory training, revised policy language, and other compliance demands.

(Image source: Eurostat)
Demographic Consideration: The gender pay gap continues to be an issue. Again, legislation comes into the picture with, for example, the passage of the Massachusetts Equal Pay Act (MEPA) in 2018, and moves by several states to ban companies from asking pre-employment questions about a candidate’s salary history.
Proactive measures taken by individual institutions such as the recent decision by the University of Eindhoven to make vacancies for academic staff exclusively open to women may also have to be taken into account.
Finally, organizations must go into the endeavour with an awareness of the time and commitment involved in completing and continuously repeating the seven steps of the planning process. It can be an expensive undertaking, leading some companies to avoid it altogether.
Human Resource Planning in Action
Ideally, HR professionals should be system and integration project managers who understand deadlines and highly complex projects.
Many academic institutions offer a degree path in Human Resources Management, and certification programs are available to qualified individuals coming from various fields.
Within the organization, employees will often work within an HR role for three to five years, before attaining management level.
(Image source: Atrivity.com)
Besides nurturing in-house talent, HR experts suggest a number of strategies for effective planning.
Organizational policies such as employment classification, benefits, compensation, performance, and improvement can assist human resource planners with the selection, training, and support of workforce members, and provide employees with guidelines for conduct and orientation in and outside the work environment.
Social media platforms like LinkedIn and Twitter can aid in recruitment and provide an engaging platform for workers to communicate with the organization and each other. But it’s important to carefully monitor these platforms and take corrective action when the social media buzz runs counter to the objectives or brand image of the business.
In terms of implementation of Human Resource Planning, the most effective organizations use proactive human resource plans, which anticipate business needs and develop strategies that achieve short-term and long-term objectives.
Such plans will employ progressive practices such as allocating a portion of the staffing budget and resources to recruitment and the hiring of key talent for future-looking projects.

Outsourcing Options for Human Resource Planning and Management
We’ve mentioned the time, effort, and expense involved in human resource planning, and these commitments may discourage smaller-scale enterprises from getting involved in the process at all.
An excellent solution to this is outsourcing HR activities for your workplace. Professional employer organizations (PEOs) can provide a viable and cost-effective alternative to in-house efforts.
PEOs operate under a “co-employment” model where the business retains effective control of its workforce, deciding whom to hire and fire, and managing their day-to-day activities. But for tax and compliance purposes, the employees appear as legal entity on the PEO’s books.
The PEO also takes responsibility for all the legal, compliance, and HR-related policy tasks that the client business defines.
NAPEO, a national organization representing PEO interests, reckons that there are roughly 900 PEOs operating in the US. Most operate on short-term contracts, usually requiring a 30-day written notice if you need to cancel their services.
With the help of PEOs, small businesses can benefit from the perks of HR planning without the hassle of spending time and cost.
Final Thoughts
Human Resource Planning plays a pivotal role in creating a smooth and efficient process for employee management and future workforce development.
Human resource planning gives business leaders more freedom to focus on meeting revenue-driving goals being fully assured that the organization’s workforce is being fully utilized towards their goals.
Any small business can make use of HR planning by effectively leveraging technology and outsourcing. Human Resources Planning enables businesses to proactively compete in the market and drive growth that is sustainable in the long run.
Summary:
Why IS Human Resource Planning Important?
- HR statistics in the US suggest that companies lose $550 billion annually due to workers feeling dissatisfied or disengaged. Businesses are therefore wise to lay greater emphasis on building a healthy organizational structure that motivates the workforce, and on promoting healthy communications between management and employees.
- Effective management and planning for human resources can assist in this. Human resource planning enables businesses to meet their current and future demands for talent, allowing human resource managers to anticipate and develop the skills most valuable to an organization, and providing the enterprise with the optimal balance of staff in terms of available skill sets and numbers of personnel.
- Proper planning also provides a path for future development by establishing a reservoir of talent capable of filling leadership roles. And in the long term, human resource planning helps align human capital management more closely with business strategy.
- HR Planning Methodology:
- Step One: Analyze the objectives of your organization
- Step Two: Make an inventory of current human resources
- Step Three: Forecast your HR demand
- Step Four: Determine the number and extent of skills gaps
- Step Five: Draw up an action plan
- Step Six: Integrate and implement the plan
- Step Seven: Monitor, measure, and offer feedback.
FAQ
A: Human resource planning is forecasting an organization’s future workforce needs and ensuring it has the right people with the right skills and positions at the right time. It is essential because it helps organizations align their human capital with their strategic goals, anticipate future talent requirements, and effectively manage their workforce.
A: Implementing human resource planning offers several benefits such as identifying skills gaps and developing strategies to bridge them. It enables effective succession planning by identifying and nurturing future leaders. It also optimizes workforce utilization, reduces recruitment costs, and minimizes disruptions caused by shortages or surpluses.
Overall, human resource planning enhances employee engagement, productivity, and retention by aligning individual aspirations with organizational goals.
A: Human resource planning contributes to business success and growth by ensuring organizations have the right talent to meet their strategic objectives. It enables organizations to proactively identify and address future talent needs, allowing for better resource allocation and workforce development.
Aligning HR strategies with business goals helps organizations build a capable and agile workforce, foster innovation, and adapt to changing market conditions, driving business success and growth.
A: Some common challenges faced when implementing human resource planning include uncertainty in future business conditions, difficulty in accurately predicting talent requirements, resistance to change from employees or management, limited budget or resources for training and development, and lack of comprehensive data for workforce analysis.
Additionally, organizations may need help integrating human resource planning with other business processes and effectively communicating the importance and benefits of HR planning to stakeholders.
A: Developing an effective human resource planning strategy involves several key steps including:
1. Analyzing the organization’s strategic goals and future workforce needs
2. Conducting a thorough assessment of the current workforce and identifying skill gaps
3. Forecasting future talent requirements
4. Developing strategies to address skill shortages or surpluses
5. Implementing recruitment and selection processes
6. Designing training and development programs
7. Establishing succession plans
8. Continuously monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the HR planning strategy