What Is Customer Experience Management (CXM)?
The world has gone digital, and opportunities for customer engagement have expanded from in-person and phone to include email, service portals, and chat. Customers now have more choices and higher expectations when choosing a business partner. They seek value through seamless, personalized interactions across various platforms and want to choose their service and support journey.
Table of Contents
ToggleCustomer experience management (CXM) is the discipline that started as a strategic marketing approach that answers this need and has grown into an area that drives customer satisfaction, loyalty, and engagement.
Successful CXM requires understanding customer interactions across multiple channels and touchpoints, analyzing customer feedback, and mapping the customer journey through the experience, leveraging this insight to deliver personalized experiences that drive customer loyalty and retention.
The Importance of the Customer in Today’s Business

This focus on customer experience has made it crucial for businesses aiming to retain and attract new customers, offering a competitive advantage to those who can master it.
By prioritizing CXM, companies can increase customer satisfaction and gain valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs. This insight can help lead to additional revenue opportunities and new markets due to better decision-making, product development, and, ultimately, a stronger bottom line.
How Does Customer Experience Management Work?
Excellent customer engagement starts with the business’s ability to understand how customers engage with them and the customer relationship they are trying to establish. These can be seen and documented by analyzing their interactions.
Once customer interactions are known and documented, the customer journey is analyzed, and standard practices adopted to ensure satisfaction are implemented for each transaction type, measured, and improved over time.
Businesses can not only improve each type of interaction based on their understanding of the customer journey, they can also look at opportunities to increase sales opportunities and service upgrades during these interactions.
When done well, the increased customer satisfaction ensures loyalty and customer engagement in an increasingly competitive landscape, as it is based on the ability to manage and improve the entire customer journey, helping to foster lasting customer relationships.
Key Components of Effective Customer Experience Management
Effective Customer Experience Management (CXM) is built on several foundational components that work together to create a seamless, positive, and personalized experience for each customer.
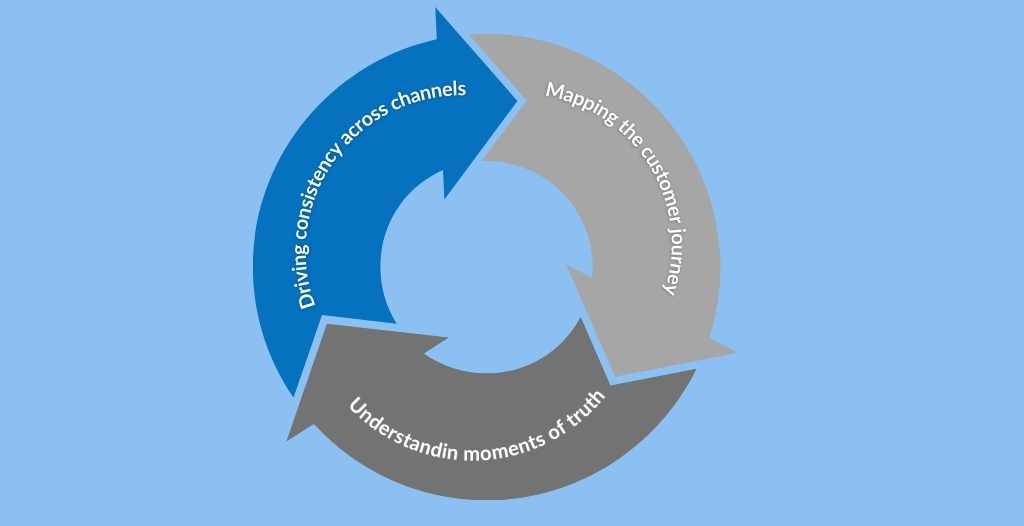
Understanding Customer Interactions
Mapping the Customer Journey: Identify and document every stage of the customer journey, from the moment they engage with your brand to the post-purchase phase, including support and advocacy. This includes understanding customers’ channels and touchpoints, such as social media, websites, retail stores, and customer service calls.
Identifying Moments of Truth: Pinpoint make or break moments in the customer journey that significantly impact the customer’s perception of the brand.
Consistency Across Channels: Ensure customers receive a consistent experience across all channels. The messaging, tone, and level of service should be uniform and responsive regardless of the channel.
Leveraging Customer Feedback and Other Data

Data Collection: Gather data from various sources, including transaction records, website analytics, social media interactions, and customer surveys. This data provides critical information about customer preferences, behaviors, and demographics.
Data Analysis: Use analytical tools and techniques to understand patterns, trends, and customer segments and use these insights to inform business decisions and CX strategies.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Apply the insights from data analysis to make informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, and customer service improvements.
Personalization During Customer Interactions

Segmentation: Divide the customer base into distinct groups (called personas) based on similar characteristics, behaviors, or needs to enable targeted and relevant communication and offerings.
Individualized Experiences: Use customer data to tailor experiences to individual preferences like personalized product recommendations, customized marketing messages, or tailored support solutions.
Predictive Personalization: Employ advanced analytics and machine learning using customer experience management software to predict customer needs and preferences, allowing the customer to engage more quickly and effectively.
Increasing Customer Loyalty Using the Customer Feedback Loop
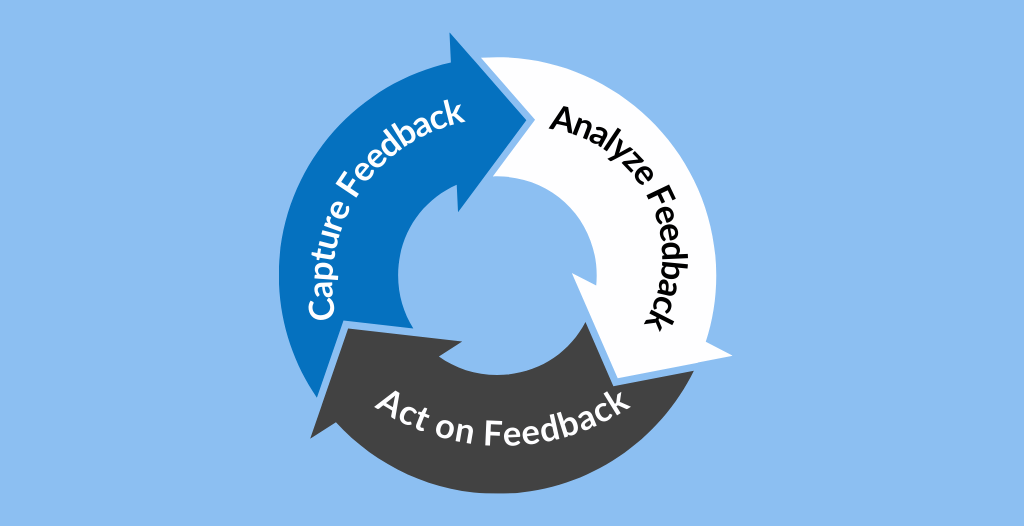
Capturing Feedback: Use customer experience management software and surveys to capture feedback across every touchpoint via surveys, feedback forms, social media monitoring, and direct engagement.
Analyzing Feedback: Identify common themes, sentiments, and areas for improvement.
Acting on Feedback: Close the loop by acting based on customer feedback. This might involve changing products or services, training staff, or improving processes.
Benefits of Implementing Customer Experience Management
Customer relationships are crucial to customer experience management success, offering numerous benefits that enhance the customer’s perception and interaction with the brand and positively impact the company’s bottom line and market position.
Companies Enjoy Increased Customer Satisfaction
Meeting Expectations: Understanding customer needs and preferences enables businesses to tailor their products, services, and interactions to meet and often exceed those expectations. The explosion of attention to Experience Level Agreements (XLAs) demonstrates the importance of meeting expectations.
Resolving Issues Proactively: CXM helps identify and address potential issues before they escalate, leading to fewer complaints and more positive experiences.
Enhancing Quality of Service: Continuous feedback and improvement lead to higher quality customer service, product offerings, and overall customer care.
Customer Loyalty is Enhanced
Personalized experiences make customers feel valued and understood, fostering an emotional connection with the brand. This helps in two ways:
Creating Advocates: Satisfied customers become brand advocates, sharing their positive experiences with others and driving word-of-mouth marketing.
Reducing Churn: By consistently delivering positive experiences, companies can reduce the rate customers leave for competitors, known as churn rate.
Companies Gain a Competitive Advantage and Differentiation
A superior CXM strategy can differentiate a brand in a crowded market by offering unique customer experiences. The emotional connection that customers experience becomes a part of the brand’s identity, increasing customer retention and brand reputation.
Focusing on customer experience often drives innovation, as companies are motivated to find new and better ways to serve their customers, giving them a competitive advantage.
Improved Financial Performance

Increased Revenue: Loyal and satisfied customers make repeat purchases and try new offerings. They often have a higher lifetime value than customers with neutral or negative feelings toward a brand.
Cost Efficiency: Retaining existing customers is generally less expensive than acquiring new ones. By increasing customer loyalty and reducing customer churn, businesses can reduce the costs associated with marketing and customer acquisition.
Market Share Growth: Companies that lead in customer experience often see growth in market share as they attract customers from competitors and enter new markets more effectively.
Additional Benefits Are Also Realized
Employee Satisfaction and Retention: Employees are more likely to enjoy their work and stay with the company when they see positive customer outcomes and receive feedback on their contributions to customer satisfaction.
Agility and Responsiveness: Companies focusing on customer experience are typically more agile and responsive to market changes. They are better positioned to adapt to customer needs and emerging trends, keeping them ahead of competitors.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management: By prioritizing customer needs and feedback, companies can also ensure better compliance with customer-related regulations and manage risks associated with customer dissatisfaction or service failures.
Strategies for Successful Customer Experience Management
Implementing a robust CXM strategy is not just about improving customer interactions; it’s a comprehensive approach that positively affects all aspects of the business, from operational efficiency and employee engagement to financial performance and market competitiveness.
Building a culture of customer service, understanding the entire customer journey, and creating a strategy include the following:
Develop a Customer-Centric Organizational Culture

The organization must offer a customer-centric organizational culture, advocated by leadership who embodies customer-centric values, ensuring these principles permeate every department and function.
This involves clear communication, training, and an organizational structure that enables the organization to align goals and incentives with customer-centric objectives.
Use CXM Technology Effectively
A great customer experience strategy is ineffective without technology that can analyze and provide valuable insights into customer transactions and feedback.
Customer experience management software and data analytics tools that provide actionable insights are a worthwhile investment, providing a comprehensive view of the customer journey and advanced solutions like AI for personalization and efficiency.
CXM technology should complement the human element, not replace it, enhancing the capability of employees to deliver personalized service.
Provide Ongoing Employee Training
Employees directly influence the customer experience and must be well-versed in CXM principles. Regular training programs should ensure all staff, from front-line to management, understand their role in shaping customer experiences.
Training should include communication, empathy, and problem-solving skills; empowering employees to make customer-centric decisions and recognizing exemplary service are also crucial.
Build a Culture of Continuous Improvement

CXM is an ongoing process, relying on qualitative data, regular evaluation, and adaptation.
Establishing feedback mechanisms is essential for capturing and analyzing customer feedback and using it to refine service processes and products.
Organizations need to collect qualitative data indicating where customer expectations have and have not been met and a program to update practices when they are not met.
Understanding the customer journeys that result in poor customer sentiment and improving them is a core activity of customer experience management.
Understanding the Difference Between CXM and CRM
Customer Experience Management (CXM) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) are two pivotal strategies in business operations that focus on customers, yet they serve distinct purposes and functions.
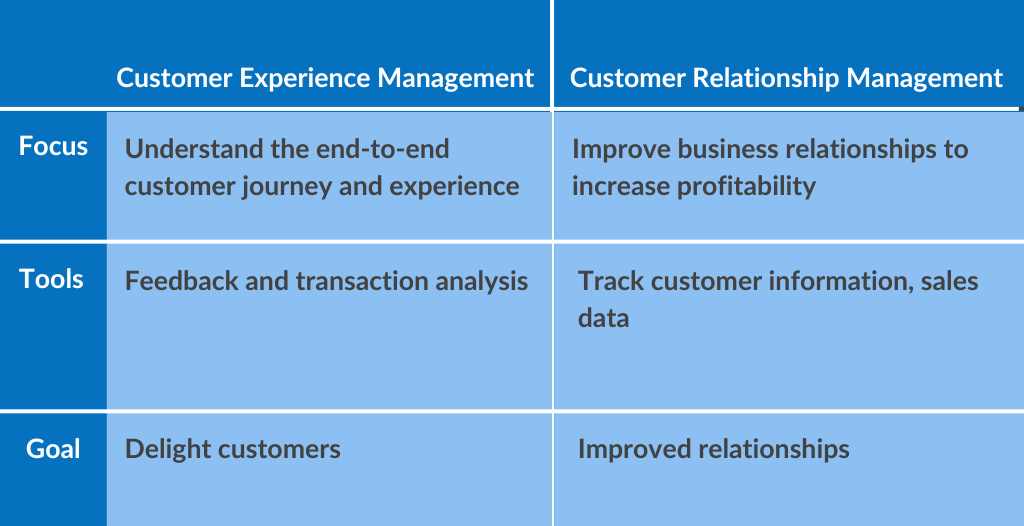
Primary Focus of CXM and CRM
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Through CRM, businesses learn more about their target audiences and how to best cater to their needs, thus driving sales growth:
CRM is a strategy and technology used by businesses to manage all interactions and relationships with potential and current customers.
The primary focus of CRM is to improve business relationships, streamline processes, and increase profitability.
CRM systems compile data from various communication channels, including a company’s website, phone, email, live chat, marketing materials, and social media.
Customer Experience Management (CXM)
CXM, on the other hand, is a broader concept that encompasses the entire experience a customer has with a business, from the first interaction to post-purchase support:
It’s about understanding the customer’s journey through all touchpoints and interactions with the brand and managing it to ensure it is as positive, consistent, and seamless as possible.
CXM aims to elevate customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy by delivering personalized and compelling experiences.
Difference Between CXM and CRM Technology and Tools
CRM tools are primarily data-driven and focus on managing customer information, sales management, productivity, and more.
They are used to store customer data, track interactions, manage customer accounts, sales leads and pipelines, and provide reporting and analytics.
CXM tools utilize transaction and qualitative data like surveys to manage the end-to-end customer experience across all channels and interactions.
They include feedback systems, analytics tools to understand customer behavior and preferences, and engagement tools to create personalized marketing and communication strategies.
Objectives and Outcomes for CRM and CXM
The main objective of CRM is to improve business relationships, increase customer retention, and drive sales growth by understanding who the customers are, managing interactions with them, and using this information to drive sales and growth.
CXM aims to provide a delightful and seamless customer experience that increases customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy by creating a positive perception of the brand throughout the customer journey, leading to organic growth through word-of-mouth and repeat business.
Scope and Business Integration
CRM tends to have a more internal focus, dealing with sales processes, customer information, and internal coordination to manage relationships and sales pipelines while the scope of CXM is broader.
The CXM scope includes internal processes but also the external interactions and perceptions customers have with the brand across all touchpoints.
While CRM and CXM are both customer-focused strategies, they serve different purposes within an organization:
CRM is about managing data and relationships to drive sales
CXM is about managing the overall customer experience to drive satisfaction and loyalty.
Both are crucial for business success and are often most effective when integrated and aligned, ensuring the insights and efficiencies gained from CRM feed into a broader, more holistic CXM strategy.
The customer experience management strategy should also include touchpoints that provide feedback into the CRM processes for changes to data collection, ensuring that insights gained through CXM are passed back into CRM.
Overcoming CXM Adoption Challenges
Adopting a successful customer experience management strategy and practice can significantly enhance customer engagement, satisfaction and loyalty but businesses often encounter several challenges that can impede successful implementation.
Understanding, addressing and embedding solutions for these challenges for them is crucial for a successful CXM initiative.
Organizations should take a strategic approach involving strong leadership, clear communication, and a commitment to customer-centric transformation.
Leaders should clearly communicate the vision for customer experience, allocate necessary resources, and regularly review and adjust strategies based on feedback and market conditions.
Organizational Silos Affect the Delivery of Great Customer Experiences

Organizational silos, where departments operate independently, can lead to inconsistent customer experiences.
A culture of collaboration and open communication between departments is critical to crossing the barriers between silos by getting employees used to working with people outside their group.
Where culture falls short, organizations may need to restructure or consolidate teams to achieve shared goals.
Company-wide adoption programs and training that stress collaboration can also help break across silos and overcome communication challenges that negatively impact customer experience management adoption.
Technology Challenges

CX technologies are rapidly changing, requiring ongoing training to keep teams updated with the latest technologies and get the most out of changes and enhancements to customer experience management software and other tools.
Ongoing technology investment and partnering with technology providers or consultants can offer additional guidance and support, making it possible to continue growing and improving the CX practice.
Data Integration and Privacy

CXM relies heavily on managing and integrating data from various sources, requiring a strong focus on cybersecurity, risk management, and data privacy laws.
Increasing data privacy and security regulations require businesses to fully understand and invest in cybersecurity platforms and asset management to protect their enterprise.
Tools are not the only focus. Organizations must also establish clear policies for data handling, ensuring compliance and ethical management of customer data.
Customer Experience Management Software
Software plays a pivotal role in enabling businesses to effectively understand, manage, and enhance the customer experience.
These tools and platforms offer a range of functionalities from data collection and analysis to customer feedback management and personalized engagement.
It’s important to understand the function and role of each type of software when planning improvements to CXM.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
CRM software is the backbone of customer interaction management, collecting and storing all customer-related data, including contact information, interaction history, purchase records, and preferences.
The centralized database leveraged for CRM allows businesses to manage relationships and interactions with current and potential customers, streamline processes, and improve profitability.
While CRM software is traditionally focused on sales and marketing, it provides an understanding of customer histories and preferences, enabling businesses to tailor their customer experience strategies more effectively.
Customer Data Platforms (CDP)
CDPs are used to consolidate and integrate customer data from multiple sources into a single, comprehensive repository.
This creates a comprehensive customer profile, including demographic information, transaction history, and digital behavior.
For CXM, these platforms:
Enable identification of the personas who do business with the organization
Provide a 360-degree view of the customer needed to deliver personalized experiences.
Allow businesses to segment customers, predict behavior, and tailor experiences across various customer touchpoints.
Experience Management Platforms
These platforms are specifically designed to manage and improve customer experiences. They include tools for mapping customer journeys, managing customer feedback, and analyzing experience data to identify areas for improvement.
Experience management platforms enable businesses to design and optimize customer journeys, manage feedback across channels, and measure the impact of CX initiatives on customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Analytics and Business Intelligence Tools
Analytics tools are used to analyze large volumes of customer data to derive insights about customer behavior, preferences, and trends. They can include predictive analytics, sentiment analysis, and customer segmentation features.
By understanding customer behavior and preferences, businesses can make informed decisions about improving the customer experience.
Analytics can also help measure CX initiatives’ success and identify improvement areas.
Marketing Automation Platforms
These platforms automate repetitive marketing tasks and enable businesses to send personalized communications to customers based on their behavior and preferences. They can manage campaigns across email, social media, the web, and other channels.
Marketing automation allows for more personalized and timely interactions, enhancing the customer experience. It ensures that customers receive relevant content and offers that resonate with their needs and interests.
Feedback and Survey Tools
Feedback is a critical component of CXM, providing direct insights into customer satisfaction and experience.
Feedback tools collect and manage customer sentiments from various channels, including surveys, social media, and direct customer interactions, and provide insights into customer satisfaction and areas for improvement.
Using these tools, businesses can capture, analyze, and act on customer feedback to continuously improve the customer experience.
Omnichannel Customer Service Platforms
These platforms provide integrated customer service across multiple phone, email, chat, and social media channels. They ensure that customer service is consistent and efficient across all touchpoints.
Omnichannel support is more than offering varied channels; these tools ensure the customer journey throughout a series of combined customer interactions and offer a smooth transition between channels.
Omnichannel platforms ensure that customers receive quick, consistent, and effective service no matter how they interact with the business.
Measuring the ROI of Customer Experience Management

To quantify the financial impact of customer experience management, businesses need to identify clear metrics and KPIs that link customer experience improvements to financial performance.
KPIs that help include customer retention rates, lifetime value, brand loyalty, and sales growth.
The financial improvements in these KPIs should be analyzed against the cost of adoption programs and CX platform implementation costs to understand the full financial benefit.
Future Trends in Customer Experience Management
Technology improvements will continue to shape customer experience management capabilities as we look to the future.
Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning, voice and conversational interfaces, emotional analytics, and hyper-personalization capabilities will provide deeper insights, improve customer service agent performance, offer additional customer channels, and provide more personalized customer experiences.
Staying ahead of these trends will enable businesses to innovate and improve their customer experience management strategies continuously.
Customer Experience Management – Final Thoughts
Customer Experience Management requires a commitment to understanding and serving customers, improving customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and advocacy, leading to sustained growth and success.
As technology evolves and customer expectations rise, the importance of effective customer experience management will only continue to grow enabling businesses that prioritize and continuously improve their CXM strategies to be well-positioned to lead in the competitive marketplace.





